EXPLANATION
This test method is an indicator of the wear characteristic of petroleum and nonpetroleum hydraulic fluids operating in a constant volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane pumps could lead to malfunction of hydraulic systems in critical applications.
TEST SUMMARY
Three gallons of a hydraulic fluid (the test requires a 5-gal sample of oil for the total run) is circulated through a rotary vane pump system for 100 h at a pump speed of 1200 r/min, and a pump outlet pressure of 13.79 MPa. Fluid temperature at the pump inlet is 65.6° C for all water glycols, emulsions, and other water containing fluids and for petroleum and synthetic fluids with viscosities of 46 cSt or less at 40° C. A temperature of 79.4° C is used for all other synthetic and petroleum fluids. The result obtained is the total cam ring and vane weight loss during the test.
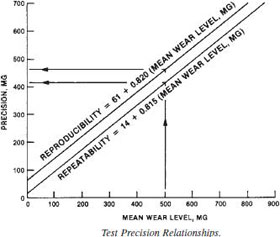
TEST PRECISION
The precision and bias of this test method are being developed. In the interim, use figure below.