EXPLANATION
This test method covers a rapid portable means for field and laboratory use to rate the ability of kerosene-type aviation turbine fuels, both neat and those containing additives, to release entrained or emulsified water when passed through fiberglass coalescing material. This test method is applicable to kerosene-type aviation turbine fuels including jet A and jet A-1 as described in Specification D1655, JP-5, JP-7, JP-8, and JP-8 + 100. This test method yields approximately the same low MSEP rating as Test Method D 3948 for fuels that contain strong surfactants as well as the products mentioned above. The Micro-Separometer has an effective measurement range from 50 to 100. Values obtained outside this limit are undefined and invalid.
TEST SUMMARY
A water-fuel sample emulsion is created in a syringe using a high-speed mixer. The emulsion is then expelled from the syringe at a programmed rate through a specific fiberglass coalescer, the MCell Coalescer, and the effluent is analyzed for uncoalsced water (i.e., dispersed water droplets) by a light transmission measurement. A test can be performed in 5 to 10 min.
INTERFERENCES - Any suspended particles, whether solid or water droplets or haze, in a fuel sample will interfere with this test method, which utilizes light transmission of a fuel sample after emulsification with water and subsequent coalescence.
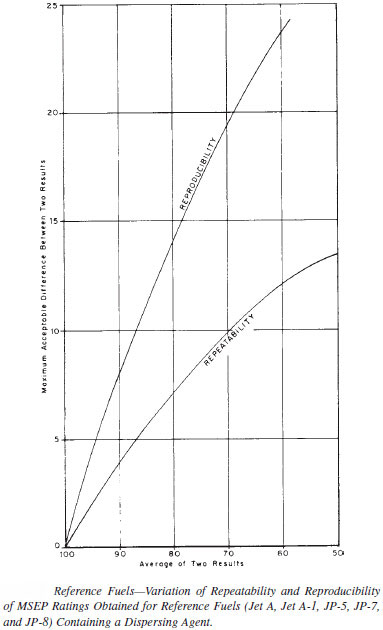
TEST PRECISION
See following figure for the repeatability and reproducibility obtained with this test method. This procedure in this test method has no bias because the value of MSEP is defined only in terms of this test method.