(Equivalent Test Methods: IP 413, ISO 8691, and DIN 51790 T3)
EXPLANATION
Knowledge of the presence of trace metals in gas turbine fuels enables the user to predict performance and, when necessary, to take appropriate action to prevent corrosion. This test method covers the determination of sodium, lead, calcium, and vanadium in Specification ASTM D2880, Grade Nos. 1-GT and 2-GT fuels in the range from 0.1 to 2.0 mg/L. This test method is intended for the determination of oil-soluble metals and not waterborne contaminants in oil-water mixtures.
TEST SUMMARY
To eliminate the problems encountered with the direct analysis of typical gas turbine fuels that exhibit significant variations in physical properties, the method of standard additions is used. Lead is determined by AAS and sodium by AAS or AES in an air-acetylene flame. Calcium and vanadium are determined by AAS or AES in a nitrous oxide-acetylene flame. If a user is interested in analyzing potassium, a procedure similar to that for sodium should be used.
Most experience with this test method is using AAS and the precision given is based on AAS measurements only.
TEST PRECISION
In the range 0.1 to 0.5 mg/L concentration, the following precision has been found for AAS measurements.
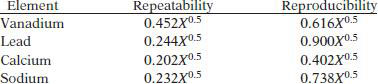
Where X is the average of duplicate results.
The bias for this method has not been determined.



