EXPLANATION
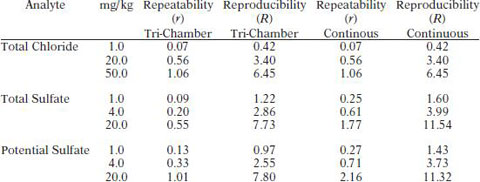
Sulfates and chlorides can be found in filter plugging deposits and fuel injector deposits. The acceptability for use of the fuel components and the finished fuels depends on the sulfate and chloride content. The method is applicable to hydrous and anhydrous denatured ethanol to be used in motor fuel applications. It is intended for the analysis of ethanol samples containing between 1.0 and 20 mg/kg of total or potential inorganic sulfate and 1.0 to 50 mg/kg of inorganic chloride.
TEST SUMMARY
For the total sulfate and chloride, a small volume of an ethanol sample is directly injected into a suitable configured ion chromatograph in accordance with manufacturer's recommendations for this test method. For potential sulfate, 0.5 mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide solution is added to 9.5 mL of the ethanol sample, and then injected into the ion chromatograph. Ions are separated based on their affinity for exchange sites of the resin with respect to the resin's affinity for the eluent. The suppressor increases the sensitivity of the test method by both increasing the conductivity of the analyte and decreasing the conductivity of the eluent. It also converts the eluent and analytes to corresponding hydrogen forms of anions. Anions are quantified by integrating their responses compared with an external calibration curve. The calibration standards are prepared in an aqueous matrix.
Interferences - Interferences can be caused by substances with similar ion chromatographic retention times, especially if they are in high concentration compared to the analyte of interest. Sample dilution can be used to minimize or resolve most interference problems.
A water dip (system void or negative peak) can cause interference with some integrators. Usually for chloride and sulfate determinations, water dip should not be a problem since their peaks are far away from the water dip.
Given the trace amounts of chloride and sulfate determined in this test method, interferences can be caused by contamination of glassware, eluent, reagents, etc. Hence, great care should be kept to ensure that the contamination is kept to a minimum.
TEST PRECISION