(Equivalent Test Method: AFNOR M07-025)
This test method covers three procedures applicable to petroleum products including lubricating oils containing additives and additive concentrates. This test method is applicable to samples boiling above 177° C and containing not less than 0.06 mass % sulfur. Petroleum coke containing up to 8 mass % sulfur can be analyzed.
For the iodate method, chlorine in concentrations <1 mass % does not interfere. The isoprene rubber method can tolerate somewhat higher levels. Nitrogen when present >0.1 mass % may interfere with the iodate method; the extent being dependent on the types of nitrogen compounds as well as the combustion conditions. It does not interfere in the IR method. The alkali and alkaline earth metals, zinc, potassium, and lead do not interfere with either method.
TEST SUMMARY
In the iodate detection system, the sample is burned in a stream of oxygen at a sufficiently high temperature to convert about 97 % of the sulfur to sulfur dioxide. A standardization factor is used to obtain accurate results. The combustion products are passed into an absorber containing an acidic solution of potassium iodide and starch indicator. A faint blue color is developed in the absorber solution by the addition of standard potassium iodate solution. As combustion proceeds, bleaching the blue color, more iodate is added. From the amount of standard iodate consumed during the combustion, the sulfur content of the sample is calculated.
In the IR detection system, the sample is weighed into a special ceramic boat which is then placed into a combustion furnace at 1371° C in an oxygen atmosphere. Most of the sulfur present is converted to sulfur dioxide which is then measured with an infrared detector after moisture and dust are removed by traps. The calibration factor is determined using standards approximating the material to be analyzed.
TEST PRECISION
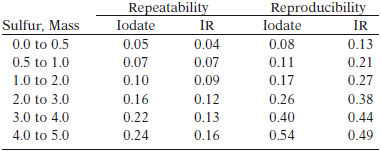
For petroleum coke, the repeatability was 0.05 X and reproducibility 0.22 X where X is the average of two test results.
The bias of this procedure has not been determined.

