EXPLANATION
These test methods (Kurt Orbahn) measure the percent viscosity loss at 100° C of polymer-containing fluids when evaluated by either of two diesel injector apparatus procedures. Procedure A uses European Diesel Injector Test Equipment and Procedure B uses fuel injector shear stability test (FISST) equipment. The viscosity loss reflects polymer degradation due to shear at the nozzle.
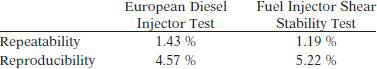
Both Procedure A (using European Diesel Injector Test Equipment) and Procedure B (using FISST equipment) of this test method evaluate the percent viscosity loss for polymer-containing fluids resulting from polymer degradation in the high shear nozzle device. Minimum interference from thermal or oxidative effects would be anticipated. The two procedures exhibit essentially equal percent viscosity loss for each oil used in developing this test method. Both procedures also show essentially comparable repeatability and reproducibility.
These test methods are not intended to predict viscosity loss in field service for different polymer classes or for different field equipment. However, it may be possible to establish some correlation for a specific polymer type in specific field equipment.
TEST SUMMARY
The polymer-containing fluid is passed through a diesel injector nozzle at a shear rate that causes the less shear stable polymer molecules to degrade. The resultant degradation reduces the kinematic viscosity of the fluid under test.
The reduction in kinematic viscosity, reported as percent loss of the initial kinematic viscosity, is a measure of the shear stability of the polymer-containing fluid.
TEST PRECISION