(Equivalent Test Methods: IP 14, ISO 4262, and AFNOR T60-117)
EXPLANATION
The carbon residue value of burner fuel serves as a rough approximation of the tendency of the fuel to form deposits in vaporizing pot- and sleeve-type burners. Similarly, provided alkyl nitrates are absent, the carbon residue of the diesel fuel correlates approximately with combustion chamber deposits. The carbon residue value of motor oils, while once considered useful, is now considered to be of doubtful value because of the presence of additives in many oils. The carbon residue of gas oil is useful as a guide in the manufacture of gas from gas oil, while the carbon residue value of crude oil residuums, cylinder and bright stocks, are useful in the manufacture of lubricants. This test method is generally applicable to relatively non-volatile petroleum products which partially decompose on distillation at atmospheric pressure.
The values obtained by this method are not numerically the same as those obtained by Test Methods ASTM D189 or ASTM D4530.
TEST SUMMARY
The sample is weighed into a special glass bulb having a capillary opening, and is placed in a metal furnace maintained at about 550° C. In this process all volatile matter is evaporated out of the bulb, and the heavier residue remaining in the bulb undergoes cracking and coking reactions. After a specified heating period, the bulb is removed from the bath, cooled in a desiccator, and again weighed. The residue remaining is calculated as a percentage of the original sample and reported as Ramsbottom carbon residue.
TEST PRECISION
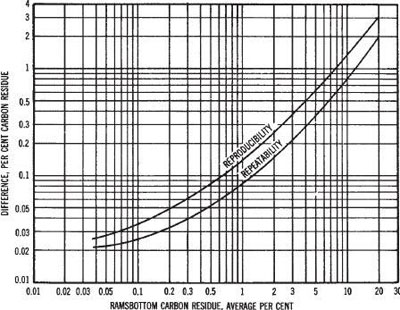
This test method is empirical and no statement of bias can be made.

