EXPLANATION
This test method provides sufficient PCB data for many regulatory requirements. While the most common regulatory level is 50 ppm, lower limits are used in some locations. This test method uses a two-tiered analytical approach to PCB screening and quantitation of liquid and solid wastes, such as oils, sludges, aqueous solutions, and other waste matrices. Tier I is designed to rapidly screen the samples for the presence of PCBs. Tier II is used to determine their concentration, typically in the range 2 to 50 ppm. Greater concentrations can be determined through sample dilutions. Quantification limits will vary depending on the types of waste streams being analyzed.
TEST SUMMARY
The sample is extracted with solvent and the extract is treated to remove interfering substances, if needed. The extract is injected into a gas chromatograph. The components are separated as they pass through the capillary column and PCB compounds, if present, are detected by an electron capture detector (ECD). For quantification, an external standard is used. The ECD has selective sensitivity to many other compounds; hence, the chromatograms obtained need to be carefully checked. Solvents, reagents, glassware, etc., may produce artifacts in the analysis. Phthalates interfere, hence, all contact of samples and extracts with plastic should be avoided. Other detectors, such as atomic emission, or mass spectrometry may be used, if sufficient performance is demonstrated.
TEST PRECISION
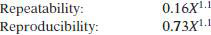
Where X is average PCB concentration in mg/kg.
This precision is based on data collected by GC/ECD.
A reliable quantitation of bias for this method was not possible. However, the method tends to produce low results. This tendency is mitigated to some extent through the use of a surrogate.



