EXPLANATION
A knowledge of spark-ignition engine fuel composition is useful for regulatory compliance, process control, and quality assurance. This test method provides for the quantitative determination of oxygenates, paraffins, olefins, napthenes, and aromatics in low-olefin spark-ignition engine fuels by multidimensional gas chromatography. The hydrocarbons can be reported by type through C10. The lower limit of detection for a single hydrocarbon component or carbon number type is 0.05 mass %. This test method is applicable for total olefins in the range from 0.05 to 13 mass %. Although specifically written for spark-ignition engine fuels containing oxygenates, this test method can also be used for other hydrocarbon streams having similar boiling ranges, such as napthas and reformates. The test method is not applicable to M85 and E85 fuels, which contain 85 % methanol and ethanol, respectively.
TEST SUMMARY
A fuel sample is injected into a computer-controlled gas chromatographic system consisting of switching valves, columns, and an olefin hydrogenation catalyst, all operating at various temperatures. The eluted hydrocarbons are detected by a flame ionization detector. The mass concentration of the detected compounds is calculated from the response factors of the detectors and normalization to 100 %. Some sulfur compounds interfere by adsorbing on the columns. Commercial dyes and detergent additives added to the fuels, and dissolved water have been found not to interfere.
TEST PRECISION
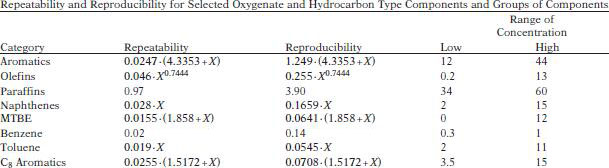
NOTE: X is the average of two results in mass % (or liquid volume %).

