EXPLANATION
The quantitative determination of olefins in spark ignition engine fuels is required by government regulations. Knowledge of the total olefin content provides a means to monitor the efficiency of catalytic cracking processes. This test method can determine olefins in the C4 to C10 range in spark ignition engine fuels or related hydrocarbon streams such as napthas and cracked napthas. Olefin concentrations in the range 0.2 to 5.0 volume % or mass % or both can be determined. Samples with higher olefins content can also be analyzed after proper dilutions. This test method is applicable to samples containing alcohols and ethers; however, samples containing greater than 15 % alcohol must be diluted. Samples containing greater than 5 % ether must also be diluted to 5 % or less level. When ethyl-ter-butyl ether is present, only olefins in the C4 to C9 range can be determined. The test method is not applicable to M85 or E85 fuels, which contain 85 % methanol and ethanol, respectively.
This test method provides better precision for olefin analysis than Test Method D1319. It is also much faster. Other alternate methods for olefin determination are Test Method D1319 which is the EPA mandated method, and Test Method D6293, which is the alternate method used for the California Air Resources Board (CARB) for this analysis.
TEST SUMMARY
A sample of fuel is injected into a computer controlled gas chromatographic system which consists of a series of columns, traps, and switching valves operating at various temperatures. The final eluted olefins are detected by flame ionization detector. Quantitation is provided by comparing the olefins' peak areas with that of an external standard. Some types of sulfur compounds may interfere by reducing the trap capacity for olefins. Commercial dyes and additives added to the fuels, and dissolved water have not been found to interfere. Free water, however, must be removed before the analysis.
TEST PRECISION
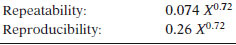
Where X is the average of two results in volume %.
Bias of this test method is not known.

