EXPLANATION
Molecular weight is a fundamental physical constant that can be used in conjunction with other physical properties to characterize pure hydrocarbons and their mixtures. A knowledge of molecular weight is necessary for the application of a number of correlative methods that are useful in determining the gross composition of the heavier fractions of petroleum. This test method can be applied to petroleum fractions with molecular weights up to 3000; however, the precision of this test method has not been established beyond 800 molecular weight. This test method should not be applied to oils having initial boiling points lower than 220° C.
TEST SUMMARY
The sample is dissolved in an appropriate solvent. A drop each of this solution and the solvent are suspended, side by side, on separate thermistors in a closed chamber saturated with solvent vapor. The solvent condenses on the sample drop and causes a temperature difference between the two drops. The resultant change in temperature is measured and used to determine the molecular weight of the sample by reference to a previously prepared calibration curve.
TEST PRECISION
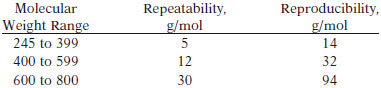
Bias for this test method has not been established.



