EXPLANATION
Ethers, alcohols, and other oxygenates can be added to gasoline to increase octane number and to reduce emissions. Type and concentration of various oxygenates are specified and regulated to ensure acceptable commercial gasoline quality. Drivability, vapor pressure, phase separation, exhaust and evaporative emissions are some of the concerns associated with oxygenated fuels. This test method determines ethers and alcohols in gasoline by gas chromatography, and is applicable to both quality control in the production of gasoline and for the determination of deliberate or extraneous oxygenate additions or contamination.
Individual ethers and alcohols are determined in the concentration range from 0.1 to 20.0, and from 0.1 to 12.0 mass %, respectively. This test method specifically excludes the analysis of alcohol-based fuels such as M-85, E-85, MTBE product, ethanol product, and denatured alcohol. Benzene while detected cannot be quantitated by this test method. Use alternate methods such as Test Methods ASTM D3606 or ASTM D4420. Oxygenates in gasoline can be determined by Test Method ASTM D5599.
TEST SUMMARY
A gasoline sample is doped with an internal standard such as 1,2-dimethoxyethane, and is injected into a gas chromatograph equipped with two columns and a column switching valve. The eluted components are detected by a flame ionization or a thermal conductivity detector. The detector response proportional to component concentration is recorded; the peak areas are measured; and the concentration of each component is calculated with reference to the internal standard.
TEST PRECISION
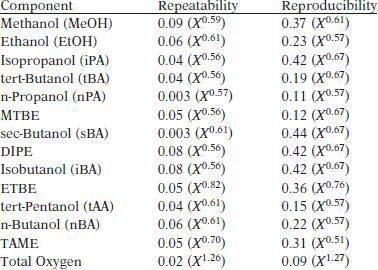
Where X is the mean mass percent of the component.

