EXPLANATION
The presence of impurities in methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) can have a deleterious effect upon the value of MTBE as a gasoline additive. Oxygenates and olefins if present are of primary concern. This test method provides for the determination of purity of MTBE by gas chromatography. Impurities are determined to a minimum concentration of 0.02 mass %. This test method is not applicable to the determination of MTBE itself in gasoline. Water cannot be measured by this test method, and must be determined by another method and the result used to normalize the chromatographic values. A majority of the impurities in MTBE is resolved by this test method; however, some co-elution is encountered. Cyclopentane and 2,3-dimethyl-butane co-elute with MTBE. However, these are not commonly found impurities in MTBE. This test method is inappropriate for impurities that boil at temperatures higher than 180 ° C or for impurities that cause poor or no response in a flame ionization detector, such as water.
TEST SUMMARY
Open tubular column gas chromatography with a flame ionization detector used in this test method is a technique that is sensitive to the contaminants commonly found in MTBE, and a technique that is widely used. Each eluting component is identified by comparing its retention time to those established by analyzing standards under identical conditions. The concentration of each component in mass percent is determined by normalization of the peak areas after each peak area is corrected by a detector response multiplication factor. The latter are determined by analyzing prepared standards with concentrations similar to those found in the sample.
TEST PRECISION
The precision of any individual measurement by this test method is expected to be dependent upon several factors such as component volatility, its concentration, and the degree of resolution from other closely eluting components. The table below lists the precision for selected representative components.
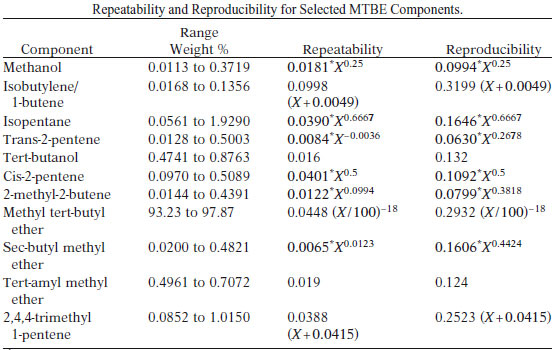
Based on the study of pure compounds, this test method was found not to have any significant bias.



