1.0 SCOPE AND APPLICATION
1.1 Method 8082 is used to determine the concentrations of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) as Aroclors or as individual PCB congeners in extracts from solid and aqueous matrices. Open-tubular, capillary columns are employed with electron capture detectors (ECD) or electrolytic conductivity detectors (ELCD). When compared to packed columns, these fused-silica, open-tubular columns offer improved resolution, better selectivity, increased sensitivity, and faster analysis. The target compounds listed below may be determined by either a single- or dual-column analysis system. The PCB congeners listed below have been tested by this method, and the method may be appropriate for additional congeners.
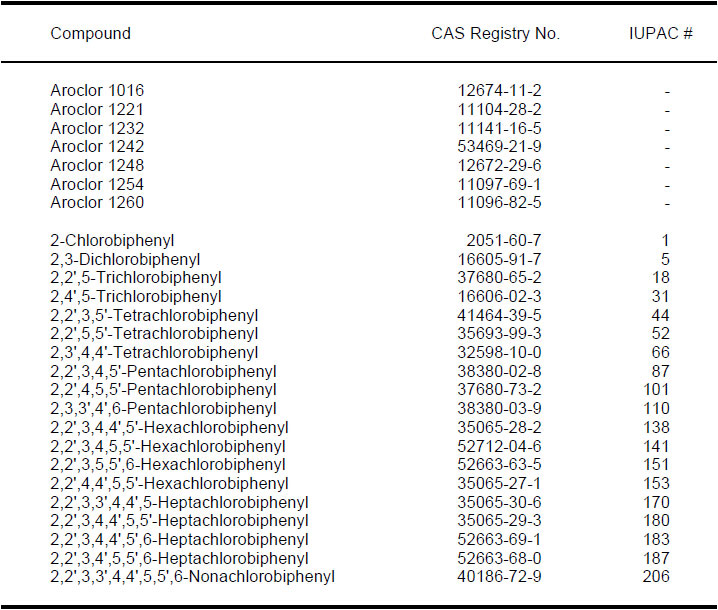
1.2 Aroclors are multi-component mixtures. When samples contain more than one Aroclor, a higher level of analyst expertise is required to attain acceptable levels of qualitative and quantitative analysis. The same is true of Aroclors that have been subjected to environmental degradation ("weathering") or degradation by treatment technologies. Such weathered multi-component mixtures may have significant differences in peak patterns than those of Aroclor standards.
1.3 Quantitation of PCBs as Aroclors is appropriate for many regulatory compliance determinations, but is particularly difficult when the Aroclors have been weathered by long exposure in the environment. Therefore, this method provides procedures for the determination of selected individual PCB congeners. The 19 PCB congeners listed above have been tested by this method.
1.4 The PCB congener approach potentially affords greater quantitative accuracy when PCBs are known to be present. As a result, this method may be used to determine Aroclors, some PCB congeners, or "total PCBs," depending on regulatory requirements and project needs. The congener method is of particular value in determining weathered Aroclors. However, analysts should use caution when using the congener method when regulatory requirements are based on Aroclor concentrations.
1.5 Compound identification based on single-column analysis should be confirmed on a second column, or should be supported by at least one other qualitative technique. This method describes analytical conditions for a second gas chromatographic column that can be used to confirm the measurements made with the primary column. GC/MS Method 8270 is also recommended as a confirmation technique when sensitivity permits (Sec. 8.0).
1.6 This method also describes a dual-column option. The option allows a hardware configuration of two analytical columns joined to a single injection port. The option allows one injection to be used for dual-column analysis. Analysts are cautioned that the dual-column option may not be appropriate when the instrument is subject to mechanical stress, many samples are to be run in a short period, or when highly contaminated samples are analyzed.
1.7 The analyst must select columns, detectors and calibration procedures most appropriate for the specific analytes of interest in a study. Matrix-specific performance data must be established and the stability of the analytical system and instrument calibration must be established for each analytical matrix (e.g., hexane solutions from sample extractions, diluted oil samples, etc.). Example chromatograms and GC conditions are provided as guidance.
1.8 The MDLs for Aroclors vary in the range of 0.054 to 0.90 µg/L in water and 57 to 70 µg/kg in soils. Estimated quantitation limits may be determined using the data in Table 1.
1.9 This method is restricted to use by, or under the supervision of, analysts experienced in the use of gas chromatographs (GC) and skilled in the interpretation of gas chromatograms. Each analyst must demonstrate the ability to generate acceptable results with this method.

