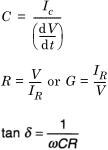4 Principle of operation
The principle of operation is to measure both the capacitive current and the conduction current by applying an alternate square wave voltage to the test cell. The capacitive current is measured during the rise time and the conduction current is measured during the stable period of the voltage, but prior to any possible disturbance of the electric field due to ion accumulation. The currents can be measured at both positive and negative half-waves of the alternate square wave voltage for a number of cycles to increase the accuracy of the measurement (see Figure 1 and [6] to [12]).
The square wave voltage V(t) of amplitude +/- V, is periodically reversed with a slope d V/dt. The current I during the rise and fall of the voltage is the sum of the capacitive current (displacement current) and the conduction current, i.e.
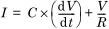
The capacitive current IC is measured during the rising and falling periods of V(t).
The conduction current IR is measured at the flat parts of V(t), since V/R<<IC, after the system has settled for a time at the beginning of each flat period. The capacitance C, the resistance R (or conductance G) and tan δ at a given angular frequency ω can be determined from the following relations: