IEC 60480 GUIDELINES FOR THE CHECKING AND TREATMENT OF SULFUR HEXAFLUORIDE (SF6) TAKEN FROM ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT AND SPECIFICATION FOR ITS RE-USE
4 Typical applications of SF6
The typical applications of SF6 are described in IEC 60376 and IEC 61634.
5 Impurities and their sources
5.1 Introductory remark
SF6 taken from electrical equipment in operation contains several kinds of impurities. Some of them are already present in the new gas, as a result of the manufacturing process. The nature of these impurities and the quantities admissible are reported in IEC 60376 and IEC 61634. The expected additional impurities in SF6 taken from equipment come from both gas handling and the operation of the equipment. Table 1 summarizes the main impurities and their sources.
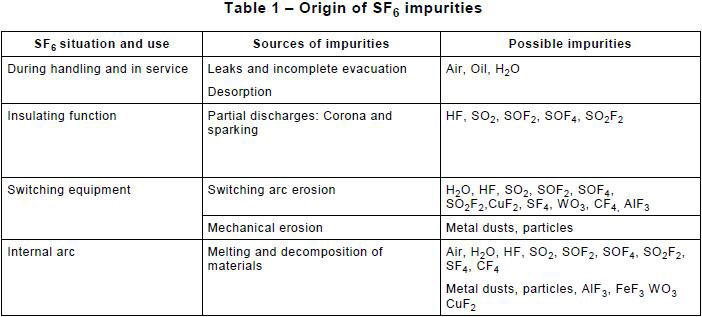
5.2 Impurities from handling and in service
Filling and emptying equipment may lead to the addition of air and water vapour.
Moisture can also be desorbed from internal surfaces of the equipment and from polymeric parts. Oil from handling equipment (pumps and compressors) may also be inadvertently introduced to SF6.
5.3 Impurities in equipment having only an insulating function
The essential process is the decomposition of SF6 by partial discharges (corona and sparking). The immediate products are fragments of SF6, such as SF5, SF4 and F, that combine with O2 and H2O to form compounds, mainly H, SO2, SOF2 , SOF4 and SO2F2. Due to low energy of the partial discharges, the accumulated quantities of these compounds are usually negligible.
5.4 Impurities in switching equipment
During current interruption, the existence of high temperature arcs leads to the formation of decomposition products of SF6, vaporized electrode metal, plastics and impurities. In addition, chemical reactions take place between the products formed (see Table 1).
The quantity of these by-products is controlled by the number of operations, the design of equipment and the use of adsorbers (solid adsorbents).
Switching equipment may also contain particles and metal dust coming from the rubbing of contacts.
5.5 Impurities from internal arcs
The occurrence of an internal arc is extremely rare. The expected impurities in SF6 in faulted equipment are similar to those normally found in switching equipment. The difference lies in the quantity of compounds, which becomes high enough to create a potential toxic risk (see IEC 61634). In addition, significant vaporization of metallic material occurs and creates additional reaction products.
6 Environmental aspects
6.1 Introductory remark
Human activities have an effect on the environment. The impact of a given activity depends on its scale and on the materials involved. It is therefore necessary to consider the possible influence of SF6 on the environment.
6.2 Impact on the ecosystem
SF6 is an inert gas. As its solubility in water is very low, it presents no danger to surface and ground water or the soil. A biological accumulation in the nutrition cycle does not occur. Therefore, SF6 does not harm the ecosystem.
6.3 Ozone depletion
SF6 does not contribute to the destruction of stratospheric ozone.
6.4 Greenhouse effect
SF6 contributes to the greenhouse effect. However, the relative amounts used are such that its contribution is less than 1 to 1 000 in comparison with other agents. Its effect is very small. Good handling practices such as those defined in this standard contribute to ensuring that a very small impact is effectively maintained over a long period of time.
6.5 Decomposition products
Decomposition products of SF6 are not released into the atmosphere in significant quantities. At the end of the service life of an item of equipment, they can be converted into naturally occurring neutral products with no adverse impact on the local environment.
6.6 Conclusion
The use of SF6 in electrical equipment has a negligible impact on the global environment and ecosystem. However, this will only remain so provided that due regard is paid by users to the containment and management of SF6 when used in electrical equipment.

