EXPLANATION
This test method is applicable to hydrocarbon mixtures including virgin, catalytically or thermally converted, alkylated, and blended napthas. The method provides for the determination of paraffins, napthenes, and aromatics by carbon number in low olefinic hydrocarbon streams having final boiling points of 200° C or less. Hydrocarbons in the boiling range 200 to 270° C are reported as a single group. Aromatics boiling at C9 and above are reported as a single aromatic group. Chemicals of a nonhydrocarbon composition may elute within the hydrocarbon groups depending on their polarity, boiling point, and molecular size. This group includes ethers and alcohols.
TEST SUMMARY
A sample is injected into a gas chromatographic system containing a series of columns and switching values. First, a polar column retains polar aromatic compounds, binapthenes, and high boiling paraffins and napthenes. The eluant from this column goes through a platinum column which hydrogenates olefins, and then to a molecular sieve column which performs a carbon number separation based on the molecular structure, that is, napthenes and paraffins. The fraction remaining on the polar column is further divided into three separate fractions that are then separated on a nonpolar column by boiling point. Eluting compounds are detected by a flame ionization detector. The mass concentration of each group is determined by the multiplication of detected peak areas by flame ionization detector response factors and normalized to 100 %.
TEST PRECISION
Based on an interlaboratory study, the following precision was obtained.
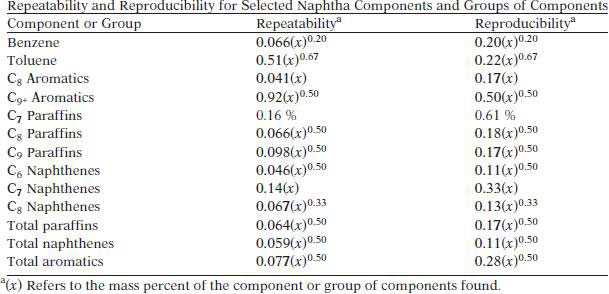
The bias of this test method has not been determined.



