(Equivalent Test Method: IP 436)
EXPLANATION
Accurate quantitative information on aromatic hydrocarbon types can be useful in determining the effects of petroleum processes on production of various finished fuels, and for indicating the quality of fuels and for assessing the relative combustion properties of finished fuels. This test method is intended to be used as one of the several possible alternative instrumental test methods that are used for quantitative determination of hydrocarbon types in fuels. This does not imply that a correlation necessarily exists between this and any other test method intended to give this information.
This test method determines mono- and di-aromatic hydrocarbon contents in aviation kerosenes and petroleum distillates boiling in the range from 50 to 300° C, such as Jet A or Jet A-1 fuels. This test method is calibrated for distillates containing from 10 to 25 % m/m monoaromatic, and from 0 to 7 % m/m di-aromatic hydrocarbons. Compounds containing sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen are possible interferents. Mono-alkenes do not interfere, but conjugated di- and polyalkenes, if present, are possible interferents.
TEST SUMMARY
The sample is diluted 1:1 with a solvent such as heptane, and a fixed volume of this solution is injected into a high performance liquid chromatograph fitted with a polar column. The column selectively separates the aromatic from the nonaromatic hydrocarbons into distinct bands in accordance with their ring structure, that is, MAHs and DAHs. The column is connected to a refractive index detector that detects the components as they elute from the column. The electronic signal from the detector is continually monitored by a data processor. The peak areas of the sample aromatics are compared with those obtained from previously run calibration standards to calculate the percent m/m MAHs and DAHs in the sample. Their sum is reported as the total aromatic content of the sample.
TEST PRECISION
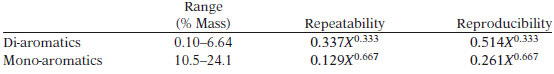
Where X is the average of results being compared.
There is no bias.



