EXPLANATION
This test method provides the determination of the amount of engine oil volatilized at 700° F (371° C). This test method is applicable to engine oils containing high molecular weight components that need not elute from a GC column. This test method can also be used to determine the amount of oil volatilized at any temperature between 238 and 371° C, if so desired. This test method is limited to samples with an initial boiling point greater than 460° F (238° C). This test gives a more precise measurement of oil volatility than that obtainable using the traditional Noack method. This test method can also be used for lubricants not within the scope of Test Method ASTM D2887.
TEST SUMMARY
The sample is mixed with an internal standard and a dilute tetracosane solution, and injected into a gas chromatograph. The column temperature is raised at a reproducible rate and the area under the chromatogram is recorded throughout the run. The retention time (RT) at 700° F is calculated using linear regression, utilizing the n-paraffins comprising the internal standard, and the tetracosane RT/boiling point data. The area response of the internal standard is related to the area of the sample determined to the 371° CRT to obtain the mass percentage of oil volatilized at 371° C.
TEST PRECISION
This test method has a repeatability of
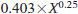 and a reproducibility of
and a reproducibility of  , where X is the volatility level.
, where X is the volatility level. 
