EXPLANATION
The boiling range distribution of medium and heavy petroleum distillate fractions provides an insight into the composition of feed stocks and products related to the petroleum refining process. The gas chromatographic (GC) simulation of this determination is used to replace conventional distillation methods for control of refining operations. This method can be used for product specification testing with the mutual agreement of interested parties. The test method is applicable to petroleum distillate fractions with an initial boiling point of < 700° C at atmospheric pressure. The test method is not applicable to products containing low molecular weight components, for example, napthas, reformates, gasolines, and crude oils. Do not use this test method for materials containing heterogenous components (for example, alcohols, ethers, esters, or acids) or residue.
This test method extends the scope of Test Method D2887 to boiling range determination by GC to include medium and heavy petroleum distillate fractions. No correlations have been established between the boiling range distributions obtained by this test method and those obtained by using Test Methods D86 or D1160.
TEST SUMMARY
A nonpolar open tubular capillary GC column is used to elute the hydrocarbon components of the sample in order of increasing boiling point. A sample aliquot diluted with a viscosity reducing solvent is introduced into the chromatographic system. The column oven temperature is raised at a specified linear rate to effect separation of the hydrocarbon components. The detector signal is recorded as area slices for consecutive retention time intervals during the analysis. Retention times of known normal paraffin hydrocarbons spanning the scope of the test method are used for normalizing the retention times of the unknown mixture area slices.
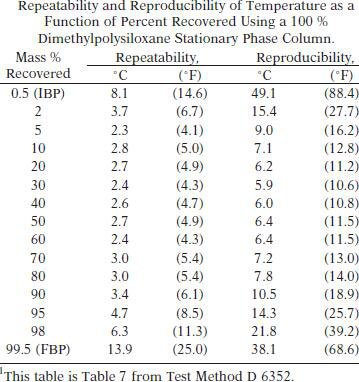
TEST PRECISION
No statement of bias can be made for this test method.

