EXPLANATION
Boiling range distribution is an essential requirement of crude oil assay. This information can be used to refinery yields, and to evaluate the economics of using one particular crude as opposed to another. The method covers boiling range distribution of water-free crude petroleum through 538° C (100° F). Material boiling above this temperature is reported as residue. The method is applicable to whole crude samples that can be dissolved in a solvent to permit sampling using a microsyringe.
This test method is faster than Test Method D2892 and can be used when only small volumes of sample are available. Also, this test method gives results up to 538° C while Test Method D2892 is limited up to 400° C. Results by both test methods are equivalent.
TEST SUMMARY
A solution of crude oil in carbon tetrachloride is injected into a gas chromatographic column that separates hydrocarbons by their boiling point order. The column temperature is raised at a reproducible and linear rate. The area under the chromatogram is recorded throughout the run. Calibration is done using a mixture of n-paraffins of known boiling point through 538° C. The amount of sample boiling above this range is estimated by a second analysis in which an internal standard is added to the crude oil.
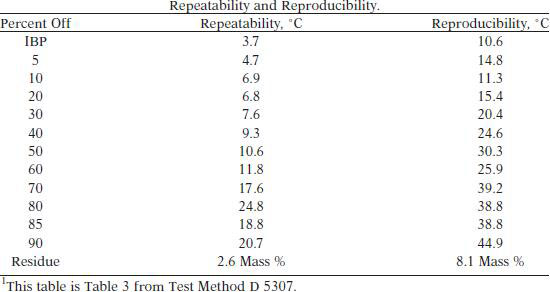
TEST PRECISION