5. Apparatus
5.1 Centrifuge Tube, cone-shaped, conforming to the dimensions given in Fig. 1, and made of thoroughly annealed glass. The graduations, numbered as shown in Fig. 1, shall be clear and distinct, and the mouth shall be constructed in a shape suitable for closure with a cork. Scale-error tolerances and smallest graduations between various calibration marks are given in Table 1 and apply to calibrations made with air-free water at 20°C.
5.2 Centrifuge, meeting all the safety requirements for normal use and capable of whirling two or more filled centrifuge tubes at a speed which can be controlled to give a relative centrifugal force (rcf) between 600 and 700 at the tip of the tubes. The revolving head, trunnion rings, and trunnion cups, including the rubber cushion, shall be soundly constructed to withstand the maximum centrifugal force capable of being delivered by the power source. The trunnion cups and cushions shall firmly support the tubes when the centrifuge is in motion. The centrifuge shall be enclosed by a metal shield or case strong enough to eliminate danger if any breakage occurs. Calculate the speed of the rotating head by means of the following equation:
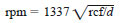
where:
rcf = relative centrifugal force, and
d = diameter of swing, in mm, measured between tips of opposite tubes when in rotating position.
Table 2 shows the relationship between diameter swing, rcf, and revolutions per minute.
6. Reagent
6.1 Hexanes, Reagent Grade. (Warning - Extremely flammable, harmful if inhaled.)
NOTE 1 - Precipitation naphtha is sometimes referred to or sold by other names, such as petroleum naphtha, petroleum ether, ligroine, petroleum benzin, and industrial naphtha. One should confirm that it meets the requirements shown in 6.1.
7. Sampling
7.1 For sampling techniques, see Practices D4057 or Practice D4177.



