12. Report
12.1 If Procedure A (Section 9) was employed, report the percentages of pentane insolubles and toluene insolubles.
12.2 If Procedure B (Section 10) was employed, report the percentages of coagulated pentane insolubles and coagulated toluene insolubles.
12.3 Insoluble resins or coagulated insoluble resins may be reported for either Procedure A or B, respectively, by subtracting toluene insolubles from pentane insolubles.
13. Precision and Bias
13.1 Precision - The following criteria should be used for judging the acceptability of results (95 % confidence):
13.1.1 Repeatability - The difference between successive test results, obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test material would, in the long run, and in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty:
13.1.1.1 Procedure A, pentane insolubles, and Procedure B, coagulated pentane insolubles:

13.1.1.2 Procedure A, toluene insolubles, and Procedure B, coagulated toluene insolubles:
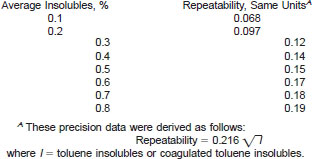
13.1.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two, single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test material would, in the long run, and in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty:
13.1.2.1 Procedure A, pentane insolubles, and Procedure B, coagulated pentane insolubles:
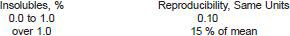
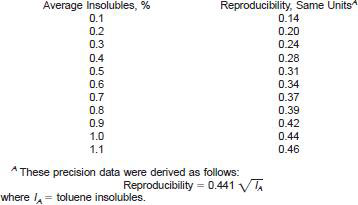
13.1.2.3 Procedure B, coagulated toluene insolubles (see Note 8):
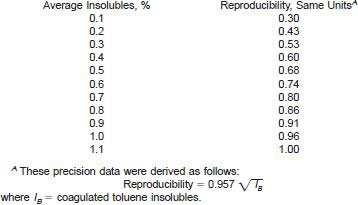
NOTE 8 - The poor interlaboratory precision (reproducibility) of this portion of this test is such that Procedure B coagulated toluene insolubles, is unsuitable for the purpose of comparison of interlaboratory results.
13.2 Bias - The procedure in this test method has no bias because the mass percent of insoluble materials can only be defined in terms of this test method.
14. Keywords
14.1 insoluble resins; insolubles; lubricating oil; used; pentane insolubles; toluene insolubles

