9.1 Make the temperature of the test specimen about the same as the test cup, then equilibrate the specimen and test cup temperature by rinsing the cup with part of the sample and filling the cup with the specimen within 15s of rinsing the cup. Record the temperature of the sample and ambient temperature. Tests conducted in a laboratory shall be done at room temperature(20 to 30°C) See Terminology D2864 for definitions.
10. Voltage Application to the Specimen
10.1 Start with the voltage across the electrodes at zero. Apply the test voltage as specified in Section 4 until operation of the interrupting equipment. Record the maximum voltage reached prior to the breakdown. If no breakdown takes place record the highest value reached and report "no breakdown" occurred.
11. Procedure
11.1 Procedure A - When it is desired to determine the dielectric breakdown voltage of a liquid on a routine basis, five breakdowns may be made on one cup filling with 1-min intervals between each breakdown and the next voltage application. The mean of the five breakdowns shall be considered the dielectric breakdown voltage of the sample, provided the range criteria of 11.3.2 is met. Retain all breakdown test values. If a second series of five breakdowns is required fill the cup with a new specimen in accordance with 8.2. During testing, maintain at least two significant digits for each breakdown.
11.2 Procedure B - When testing dielectric liquids described in 1.4.2.1 to determine dielectric breakdown or when comparing breakdown results with other test facilities, make one breakdown on each of five successive fillings of the test cup. The mean of the five breakdowns maybe reported as the breakdown voltage, provided the range criteria of 11.3.2 is met. Retain all breakdown values. During testing maintain at least two significant digits for each breakdown.
11.3 Criteria for Statistical Consistency:
11.3.1 Calculate the mean of the 5 or 10 breakdowns using the following equation:
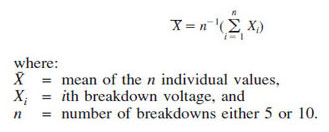
11.3.2 Acceptable Range Criteria - Using the breakdown values, determined in 11.1 or 11.2, calculate the mean breakdown value using the equation in 11.3.1. Determine that the range of the five breakdowns is no greater than 92% of the meanvalue. If the range is acceptable, report this mean value as the dielectric breakdown voltage. If the range exceeds 92% of the mean value of the five breakdowns, then conduct five additional breakdowns in accordance with 11.1 or 11.2. Obtain the new mean breakdown value for the ten breakdowns. Determine the range of the ten breakdowns and if the range is less than 151% of the mean value of the ten breakdowns, report this mean value as the dielectric breakdown voltage for the sample. If the allowable range is exceeded, the error is too large. Investigate the cause of the error and repeat the tests.
12. Report
12.1 Report the following in formation:
12.1.1 ASTM designation of the test method used(D877),
12.1.2 Procedureused: Procedure A or Procedure B,
12.1.3 The type of fluid tested,
12.1.4 Temperature of the sample recorded at collection and of the specimen when tested, and
12.1.5 Individual breakdown values and the mean breakdown.
12.1.5.1 Number of breakdowns, either 5 or 10.
12.1.6 If the sample was observed to contain free water, the report should so indicate, with a statement that the test was not made.
13. Precision and Bias
13.1 Single-Operator Precision - The single-operator percent coefficient of variance of a single test result comprised of 5 breakdowns has been found to be 10.7%. Therefore, results of two properly conducted tests by the same operator on the same sample should not differ by more than 30.3% of the mean of the two tests. The maximum allowable range for the series of 5 breakdowns should not exceed 92% of the mean of the 5 breakdowns. The maximum allowable range for the series of 10 breakdowns should not exceed 151% of the mean of the 10 breakdowns.
13.2 Multilaboratory Precision - The multilaboratory percent coefficient of variance has been found to be 10.7%. Therefore, results of two properly conducted tests indifferent laboratories on the same sample of oil should not differ by more than 30.3% of the mean of the two results.
13.3 Bias - No statement can be made about the bias of this test method because a standard reference material is not available.
14. Keywords
14.1 breakdown voltage; dielectric strength; disk electrodes; electrical insulating liquids; test cup

