ASTM D850 Standard Test Method for Distillation of Industrial Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Materials
10. Procedure
10.1 Manual Distillation Procedure:
10.1.1 Connect the flask to the condenser apparatus as described in Section 9. Fit the thermometer to the flask as described in 9.1.
10.1.2 Heat the flask slowly, especially after boiling has begun, so as to allow the mercury column of the thermometer to become fully expanded before the first drop distills over. Regulate the rate of heating so that the ring of condensing vapor on the wall of the flask reaches the lower edge of the side arm in not less than 90 s, and preferably approximately 120 s, from the start of the rise of the vapor ring. The total time from the start of heating until the first drop falls into the receiver should be not less than 5 nor more than 10 min. Avoid major changes in heating rate. Even operation is best gained through experience with the method. When distillation starts, adjust the receiver to allow condensation to flow down its inner wall to prevent loss by spattering; then adjust the heater to continue the distillation at the rate of 5 to 7 mL/min (about 2 drops/s). Maintain this rate, and continue the distillation to dryness. The total yield of distillate when testing close boiling benzenes, toluenes, and xylenes shall be not less than 97 %, and when testing wider boiling refined products and light oils, shall be not less than 95 %; otherwise, the test shall be repeated.
10.1.3 Take the temperature reading when the first drop of distillate falls into the receiving cylinder and report as the initial boiling point (IBP). If necessary, take additional readings when 5, 10, each additional 10 up through 90, and 95 % of the specimen has just distilled over. Take a final reading when the liquid just disappears from the lowest point in the flask, and report this reading as the dry point temperature. When testing crude materials, a decomposition point, rather than a dry point, may be obtained. When a decomposition point is reached at the end of a distillation, the temperature will frequently cease to rise and begin to fall. In this case, take the temperature at the decomposition point as the maximum temperature observed. The decomposition point may also be indicated by the appearance of heavy fumes in the flask. Should that occur, record the temperature at the time the bulb of the flask becomes substantially full of fumes. If a decomposition rather than a dry point is observed, so note when recording results.
10.1.4 Observe and record any correction for inaccuracy of the thermometer at the time and place of the distillation test.
10.2 Automatic Distillation Procedure:
10.2.1 Connect the distillation flask to the automatic distillation equipment as described in 9.2. Fit the temperature measuring device to the flask for automatic distillation equipment according to the manufacturer's instructions.
10.3 Barometer Reading and Temperature of the Barometer - The observed barometric pressure shall be corrected by reference to standard tables and reported in terms of millimeters of mercury at 0°C.
11. Temperature Corrections
11.1 Corrections of temperature should be applied in the following cases:
11.1.1 When required by the specifications,
11.1.2 When there is any question of compliance with the specifications, and
11.1.3 When tests of the sample are to be checked against results obtained by another investigator.
NOTE 3 - When corrected temperatures are reported, notation should be made of the type of corrections applied.
11.2 Inaccuracy of Thermometer - This correction shall be obtained by calibration of the thermometer used in the test and applied to the observed thermometer reading.
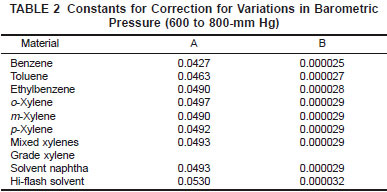
11.3 Variation from Standard Barometric Pressure - This correction shall be applied to the observed temperature after correcting for inaccuracy of the thermometer and is determined by the following equation:
C = [A + {B X (760 - P)}] X (760 - P)
where:
C = the correction in degrees Celsius,
A, B = constants from Table 2,
P = the measured barometric pressure in millimetres of mercury corrected to 0°C.
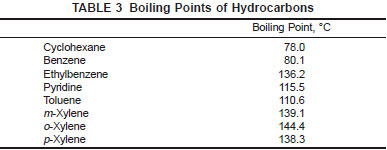
11.4 Combined Corrections - If the overall distillation range of the sample does not exceed 2°C, a combined correction for thermometer inaccuracy and barometric pressure may be made on the basis of the difference between the observed 50 % boiling point and the true boiling point at 760 mm as given in Table 3.