10. Quality Control
10.1 Confirm the performance of the instrument or the test procedure by analyzing a QC sample (see 6.8).
10.1.1 When QC/Quality Assurance (QA) protocols are already established in the testing facility, these may be used to confirm the reliability of the test result.
10.1.2 When there is no QC/QA protocol established in the testing facility, Appendix X1 can be used as the QC/QA system.
11. Precision and Bias
11.1 The precision of this test method is not known to have been obtained in accordance with currently accepted guidelines (for example, in Committee D-2 Research Report RR:D2-1007, Manual on Determining Precision Data for ASTM Methods on Petroleum Products and Lubricants).
11.2 The precision of this test method as obtained by statistical examination of interlaboratory test results is as follows:
11.2.1 Repeatability - The difference between successive test results obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test material would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method exceed the following values only in one case in twenty:
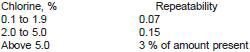
11.2.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test material would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method exceed the following values only in one case in twenty:

11.3 Bias:
11.3.1 Cooperative data indicate that deviations of test results from the true chlorine content are of the same order of magnitude as the reproducibility.
11.3.2 It is not practicable to specify the bias of this test method for measuring chlorine because the responsible sub-committee, after diligent search, was unable to attract volunteers for an interlaboratory study.
12. Keywords
12.1 bomb; chlorine

