14. Report
14.1 Report silicon concentration of the test sample calculated from Section 13 using units of mg/kg, rounded to the nearest 0.1 mg/kg for concentrations <100 mg/kg, and rounded to the nearest 1 mg/kg for concentrations ≥100 mg/kg. Indicate that the results were obtained according to Test Method D7757.
15. Quality Control
15.1 It is recommended that each laboratory establish a program to ensure that the measurement system described in this test method is in statistical control. One part of such a program might be the regular use and charting of quality control samples (see 7.5). It is recommended that at least one type of quality control sample be analyzed that is representative of typical laboratory samples as defined in Practice D6299.
15.2 In addition to running a quality control sample (see 7.5), it is strongly recommended that the calibration blank (for example, isooctane) be analyzed on a daily basis when samples are being analyzed on a given day.
15.2.1 The measured concentration for the blank should be less than 1 mg/kg silicon. Ifthe measured concentration for the blank is greater than 1 mg/kg, re-standardize the instrument and repeat the measurement of the blank (use a fresh sample and fresh cell). If the result falls outside the acceptable range, carry out a full calibration. If the sample loading port becomes contaminated, especially when analyzing <20 mg/kg silicon level samples, it is necessary to open and clean it according to manufacturer's recommendations before further use.
15.3 Results Validation - Once a standard or sample has been measured, a procedure should be carried out to validate that measurement. This requires the operator to check for obvious signs of damage to the sample such as leaking sample cells and inspection of any secondary film.
15.4 Observation of the Resultant Analysis - If a result is considered outside normal thresholds, a repeat of the analysis should be carried out to confirm anomalous results.
15.5 Regular checks should be carried out to ensure that purging gas performance is within the instrument manufacturer's specification.
15.6 Drift and quality control standards/monitors shall be run on a regular basis. The tolerance level of the checks made using these monitors should be such that a protocol of either drift correction or total recalibration is carried out if the results fall outside these levels. All measurements should be repeated between the last accepted monitor result and point of non-compliance should a current monitor measurement prove to be outside acceptable levels.
16. Precision and Bias
16.1 Precision - The precision of this test method was determined by statistical examination of an interlaboratory study, in accordance with Practice D6300. Precision was calculated by using data from seven laboratories, using seven newly manufactured analyzers, which each analyzed 24 silicon-doped samples in the range of 3 mg/kg to 100 mg/kg. The samples included 6 gasolines, 4 gasolines with 10 % ethanol, 2 naphthas, 2 toluenes, 4 E85, and 6 E100 samples. Samples were analyzed in duplicate and back-to-back. A pooled limit of quantitation (PLOQ) of approximately 3 mg/kg was determined for all sample types.
16.1.1 Repeatability - The difference between successive results obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test material would in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in 20:
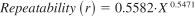
where:
X = silicon concentration in mg/kg total silicon. See Table 3 for calculated values.
16.1.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on different equipment on identical test material would in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in 20:
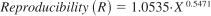
where:
X = silicon concentration in mg/kg total silicon. See Table 3 for calculated values.
16.2 Bias - Since there is no accepted reference material suitable for determining the bias in this test method for measuring silicon, bias has not been determined.
17. Keywords
17.1 analysis; ethanol; fuel; gasoline; monochromatic X-ray; MWDXRF; silicon; spectrometry; wavelength dispersive X-ray fluorescence; WDXRF; X-ray



