12. Procedure
12.1 Place the crude oil sample containers in an ultrasonic homogenizer for approximately 15 min just prior to analysis. Keep the water in the bath at ambient temperature by adding a few ice chips as the temperature rises. The homogenization step dissociates particulate mercury and promotes a more stable suspension.
12.2 Remove the sample boat and reagents (if required) from the muffle furnace and allow to cool to room temperature in a covered container.
12.3 If required for the analysis, spread approximately 1 g of Reagent 1 (aluminum oxide) in the bottom of a cooled sample boat.
12.4 Shake the sample to mix just before withdrawing an aliquot. Open the cap and quickly withdraw sample in a clean disposable transfer pipette. Weigh approximately 0.1 g of the sample into the sample boat, spreading the liquid over Reagent 1 already in the boat. Cover the sample evenly with another 1 g of Reagent 1.
12.5 Evenly spread approximately 3.5 g of Reagent 2 in the sample boat over the layer of Reagent 1 and sample.
12.6 Choose appropriate instrument parameters and heating mode for crude oil based upon manufacturer's instructions.
12.7 Open the inlet cover. Insert the sample boat into the combustion area of the furnace. Close the cover and start the analysis. Analyze a test specimen of the analysis sample in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
12.8 After the analysis is complete, remove the sample boat from the furnace. Allow to cool before disposing the reagent material. Rinse the residue from the sample boat with water and return it to muffle furnace to condition the boat for the next analysis.
13. Calculation
13.1 Calculate the concentration of mercury, on the appropriate sample basis, as follows:
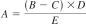
where:
A = ng/g of the analyte,
B = detector response for the analyte,
C = detector response for the reagent blank,
D = mass, ng per unit of detector response established for analyte during calibration, and
E = mass of test specimen, g.
13.2 The calculations can be provided automatically by the instrumental system used for this test method.

