5. Apparatus
5.1 Automated Viscometer - The system shall consist of the following components:
5.1.1 Viscometer Bath:
5.1.1.1 Bath, to ensure optimal thermal equilibration of the system, the bath is filled with mineral or silicone oil and equipped with a stirring device.
5.1.2 Temperature Regulation System, to control the bath temperature to within 0.02 °C.
5.1.3 Houillon Viscometer Tubes, made of glass with a calibrated volume which varies depending on the tube size (see Fig. 2). This technique allows the viscosity to be measured over a wide range of values (see Fig. 1).
5.1.4 Cleaning/Vacuum System, consisting of one or more solvent reservoirs to transport the solvent(s) to the viscometer tubes, dry the viscometer tubes after the flushing cycle, to remove the sample, and for drainage of waste products.
5.1.5 Automated Viscometer Control System - Suitable electronic processor capable of operating the apparatus, controlling the operation of the timers, regulating the bath temperature, cleaning the viscometer tubes, and recording and reporting the results.
5.1.6 PC-compatible Computer System, may be used for data acquisition, as per manufacturer's instructions.
5.1.7 Timing Devices - Use any timing device that is capable of taking readings with a discrimination of 0.01 s or better with an accuracy within +/- 0.07 % of the reading when tested over the minimum and maximum intervals of expected flow times.
5.1.8 Volume Delivery Device, such as a micropipette, capable of delivering a sufficient volume of sample to the Houillon tube being used. (See Fig. 1 for approximate sample volumes.)
5.2 Temperature Measuring Devices - Use either calibrated liquid-in-glass thermometers, of an accuracy after correction of +/- 0.02 °C or better, or other thermometric devices such as a digital contact thermometer as described in 5.2.1 with equal or better accuracy.
5.2.1 Digital Contact Thermometer Requirements:
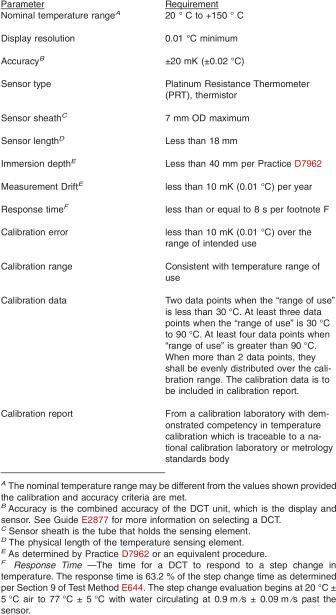
5.2.2 Measurement Drift - The drift in calibration should be checked periodically and at least once per year. This can be accomplished using Practice D7962 or Test Methods E644. When a DCT's calibration drifts in one direction over several checks against a reference temperature, such as the ice point, it may be an indication of deterioration of the DCT. The probe is to be recalibrated when the check value differs by more than the drift listed in 5.2.1 since the last probe calibration. See Practice E563, Test Methods E644, or Guide E1750 for more information regarding checking calibrations.
5.2.3 It is preferable for the center of the sensing element to be located at the same level as the lower half of the working capillary as long as the minimum immersion requirements are met.
6. Reagents and Materials
6.1 Certified viscosity reference standards shall be certified by a laboratory that has been shown to meet the requirements of ISO/EC 17025 by independent assessment. The certified viscosity reference standards shall be traceable to master viscometer procedures described in Test Method D2162.
6.1.1 The uncertainty of the certified viscosity reference standard shall be stated for each certified value (k = 2 @ 95 % confidence). See ISO 5725 or NIST 1297.
6.2 Non-chromium-containing, strongly oxidizing acid cleaning solution. (Warning - Non-chromium-containing, strongly oxidizing acid cleaning solutions are highly corrosive and potentially hazardous in contact with organic materials, but do not contain chromium which has special disposal problems.)
6.3 Solvent(s) for cleaning, drying, reagent grade. Refer to manufacturer's recommendations. Filter before use if necessary. Typical solvent(s) include:
6.3.1 Toluene. (Warning - Flammable. Vapor harmful.)
6.3.2 Petroleum spirit or naphtha. (Warning - Flammable. Health hazard.)
6.3.3 Acetone. (Warning - Extremely flammable. Health hazard.)
6.3.4 Heptane. (Warning - Flammable. Health hazard.)
6.4 Technical grade silicone oil or white oil of appropriate viscosity (for example, about 100 mm2/s @ 25 °C or equivalent) to maintain the test temperature.

