8. Procedure
8.1 The voltammetric analyzer used in this test method gives linear results between 2 to 50 mmol for hindered phenols and aromatic amines using an oil sample size of 0.40 mL and 5.0 mL of the analysis test solution. The corresponding range of mass % depends on the molecular weight of the hindered phenol and aromatic amine, and the density of the base oil. For instance, the mass % range of 0.044 to 1.1 is equal to 2 to 50 mmol/L for a hindered phenol containing one hydroxyl group and with a molecular weight of 220 g/mol (2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol) and an oil density of 1 g/mL. Below 2 mmol, the noise to signal ratio becomes large, decreasing the accuracy of the measurements. For measurements below 2 mmol or for fresh oils with high noise to signal ratios, the sample size should be increased to 0.60 mL and the volume of analysis test solution decreased to 3.0 mL.
8.2 General Voltammetric Test Procedure - The test procedure for voltammetric analysis will consist ofthe blank reading (calibration), followed by a standard reading, and finally the sample (in-service oil) reading.
8.2.1 Blank Reading - (0 mmol/L = 0 mass %).
8.2.1.1 The blank reading (voltammetric number) is a measurement of the analysis test solution by itself. The blank measurement gives a reference number with no antioxidant present (the zero baseline).
8.2.2 Standard Reading - (30 to 150 mmol/L - mass % dependent on density of fresh oil and molecular weight of antioxidant).
8.2.2.1 The standard reading is a measurement of a fresh, unused oil (containing hindered phenol and amines antioxidants) mixed with an appropriate analysis test solution. This measurement gives you a voltammetric reading (standard reading) that indicates the voltammetric response for the concentration hindered phenol and aromatic amines antioxidants being analyzed for the oil being tested.
8.2.3 Sample (In-service Oil) Reading.
8.2.3.1 The sample reading is a measurement of a fresh or in-service oil mixed with the same type of analysis test solution as the standard. This measurement will provide voltammetric readings that normally range between the blank and standard measurements, and reflect the concentration of hindered phenol and aromatic amine antioxidant present (fresh oil) or remaining (in-service oil) in the oil sample. Voltammetric readings for in-service oils will decrease as hindered phenol and aromatic amine antioxidants are depleted.
8.3 Voltammetric Reading - After the operator has selected the valleys before and after the antioxidant peaks (as shown in Fig. 1), the software (R-DMS) will automatically identify and calculate the area above the baseline between the two valley indicators. This calculated area is then used for the sample reading (in-service oil), which will be established by comparing the in-service oil area to its standard (see Fig. 3) and make remaining antioxidant calculations (see Section 9).
8.3.1 If peak shifting is occurring, it is advised to repeat the voltammetric test after performing the cleaning of the electrode. If after this second test the peak shifting is occurring again, it is advised to drag the valley indicators manually to their shifted locations.
8.4 Calibration (Blank Reading) Procedure - Pipette 5.0 mL of analysis test solution into a 7 mL vial or other suitable container containing 1 g ofsand. Insert the electrode of the voltammetric analyzer into the analysis test solution to wet the bottom surface of the electrode, remove, and rub dry the bottom electrode surface with a lint free paper towel. Insert the electrode into the vial so that the bottom of the electrode is submerged in the analysis test solution without resting on the sand layer on the bottom of the vial. Place the vial/probe upright into rack or foam block for testing. Perform the voltammetric analysis (see 5.1). Record the voltammetric reading in the voltage range of aromatic amines, 0.8 to 1.2 V (see Note 1) and the phenols, 1.3 to 1.6 V (see Note 1) in neutral test solution (Fig. 1). Remove the combination electrode from the blank test solution and rub dry the bottom surface of the electrode with a lint free paper towel. Run at least two tests of the analysis test solution to ensure the electrode is clean and the minimal blank value has been obtained.
8.4.1 Calibration Frequency - Recalibration with freshly prepared blank test solution shall be performed before each testing session.
8.5 Standard and In-service Oil Sample Preparation Procedures
8.5.1 Steps:
8.5.1.1 Preparing Test Solution Step - Remove seal and cap of the test solution vial. Pipette 5.0 mL of analysis test solution into a 7 mL vial or other suitable container containing 1 g of sand. Pipette 0.40 mL of the selected oil sample also into the 7 mL vial.
8.5.1.2 For measurements below 2 mmol or fresh oils with high noise-to-signal ratios, the sample size should be increased to 0.60 mL.
8.5.1.3 Shaking Test Solution Step - Cap the vial and shake vigorously using a vortex mixer for 20 s or by hand (between 50 and 60 shaking cycles/min.), until sand is thoroughly mixed. Place the prepared oil test solution upright in a rack or perforated foam block for a minimum time of 30 s to allow the sand to settle on the bottom of the vial with the oil.
8.5.1.4 Cleaning Electrode Step - Prepare the electrode for analysis by cleaning it. Use an alcohol-cleansing pad to wet the bottom surface of the electrode. The bottom of the electrode must be dried immediately with a clean lens tissue (lint free paper towel). The glassy carbon surface should always have a polished look before running a test. A glazed or cloudy look indicates the presence of a chemical film. If the probe tip is not cleaned properly, voltammetric readings can be distorted.
8.5.1.5 Running Test Step - Insert the electrode into the vial so that the bottom of the electrode is submerged in the analysis test solution without resting on the sand layer on the bottom of the vial. Place the vial/probe upright into a rack or foam block for testing. Perform the voltammetric analysis (see 5.1) for hindered phenolic and aminic antioxidants. Record the valley to valley antioxidant readings in the voltage range of the amines, 0.8 to 1.2 V (see Note 1) and the phenols, 1.3 to 1.6 V (see Note 1) in the neutral test solution (Fig. 1). Remove the combination electrode from the oil test solution and repeat the cleaning procedure of the electrode. Run at least two tests (cleaning the electrode and shaking the standard for 10 s between tests) ofthe standard or in-service oil sample to ensure the value is stable and repeatable.
8.5.1.6 Make all measurements within 5 min after the initial mixing of the analysis test solution, selected sample, and sand.
8.5.2 When the manufacturer of the oil is known, and the uninhibited base oil is available, use it to prepare the standards (mmole or mass % antioxidant calculations). Prepare a standard containing in the range of 30 to 150 mmol/L of oil (0.5 to 3.0 mass %) of the selected phenolic and aminic antioxidant dissolved in an uninhibited base oil. The concentration should be selected to span the expected concentrations of the new and in-service oils.
8.5.3 Standard readings should be updated whenever new batches of lubricants are stocked, and checked periodically to monitor the amount of natural oxidation occurring in the stock during storage.
8.5.4 For fresh or in-service oils of unknown origin, use a typical fresh turbine oil as the standard (100 % remaining antioxidant calculations).
8.5.5 The analysis test solution and scan time should be the same for the blank, standard, and in-service oil sample.
9. Calculations
9.1 Percent Hindered Phenol and Aromatic Amine Antioxidant Calculation - If the hindered phenol and aromatic amine, antioxidant present in the oil sample is known, then the percent hindered phenol and aromatic amine antioxidant in the sample can be calculated as follows:

where:
reading = valley to valley area (see 8.3) for antioxidants peaks between 0.8 to 1.6 V (see Note 1)
9.2 Molar Concentration of Hindered Phenol and Aromatic Amine Antioxidant Calculation - If the hindered phenol and aromatic amine antioxidant in the oil sample is unknown, then the millimoles of hindered phenol and aromatic amine antioxidant in the sample can be calculated as follows:

where:
reading = valley to valley area (see 8.3) for antioxidants peaks between 0.8 to 1.6 V (see Note 1)
9.3 Percent Remaining Hindered Phenol and Aromatic Amine Antioxidant Calculation - Calculate the percent remaining antioxidant in an in-service oil using the fresh oil as the 100 % standard with the following calculation:
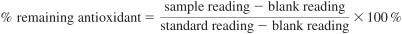
where:
reading = valley to valley area (see 8.3) for antioxidants peaks between 0.8 to 1.6 V (see Note 1)



