4. Summary of Test Method
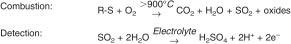
4.1 The sample is injected at a controlled rate into a stream of inert gas (helium or argon) or inert gas mixed with oxygen. The sample is vaporized and carried into a high temperature zone (>900°C) where oxygen is introduced. Sulfur compounds, present in the specimen are converted to sulfur dioxide (SO2). Sulfur dioxide is reacted with the sensing electrode in a 3-electrode electrochemical cell. This reaction produces a measurable current that is directly proportional to the amount of sulfur in the original sample material. The reactions that occur are as follows:
5. Significance and Use
5.1 All sulfur present in petroleum products is converted to sulfur oxides upon combustion, which is a significant pollutant of the atmosphere. This test method can be used to monitor the total sulfur levels in these fuels.
NOTE 1 - Virtually all sulfur compounds will be detected by this technique.
6. Interferences
6.1 Moisture produced during the combustion step can interfere if not removed prior to the detector.
6.2 Equivalent amounts of nitrogen in the sample may also interfere.



