ASTM D664 for acid number of petroleum products by potentiometric titration
12. Calculation
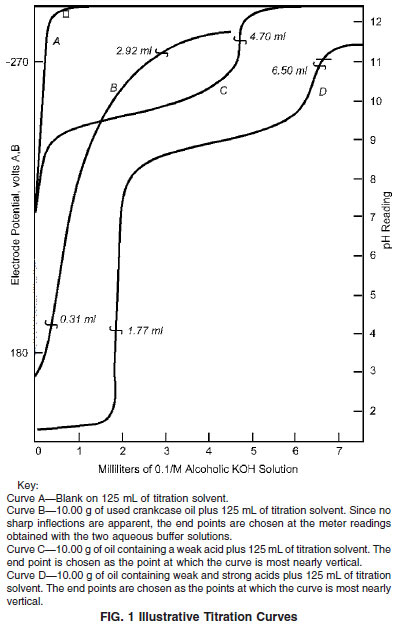
12.1 Manual Titration - Plot the volumes of the 0.1-mol/L alcoholic KOH solution added against the corresponding meter readings (see Fig. 1). Mark as an end point only a well-defined inflection point (see Note 16) that is closest to the cell voltage corresponding to that obtained with the aqueous acidic or basic buffer. If inflections are ill defined or no inflection appears (see Fig.1, Curve B), mark the end point at the meter reading corresponding to that obtained with the appropriate aqueous buffer.
NOTE 16 - One inflection point is generally recognizable by inspection whenever several successive 0.05-mL increments each produce a cell potential change greater than 15 mV at least 30 % greater than those produced by previous or subsequent increments of the same size. Generally, definite inflection points may be discerned only in regions where increments of the same size are used.
12.1.1 Some additive chemistry may produce an inflection point beyond the buffer endpoint. For additives, take the last inflection point for calculation. If using an automatic titrator, a change in the instrument parameters may be required to detect this type of endpoint.
12.1.2 For all acid titrations on used oils, mark as an end point, the point on the curve that corresponds to the meter reading for an aqueous basic buffer (pH 11) and the meter reading for the aqueous acid buffer (pH 4) when strong acids are indicated.
NOTE 17 - The cooperative work done on acid number determinations on fresh oils, additive concentrates, and used oils indicated well-defined inflection points for fresh oils and additive concentrates, and generally ill-defined inflections, or no inflection points at all, for used oils.
12.2 Automatic Titration Method - Mark the end points on the curves obtained in 11.4, in the same way as for the manual titration method.
12.3 Method of Calculation - The method of calculation in 12.3.1 is applicable to both manual and automatic methods.
12.3.1 Calculate the acid number and strong acid number as follows:
Acid number, mg KOH/g = (A - B) x M x 56.1/W
Strong acid number, mg KOH/g = (CM + Dm) x 56.1/W
where:
A = volume of alcoholic KOH solution used to titrate sample to end point that occurs at the meter reading of the inflection point closest to the meter reading corresponding to the pH 11 aqueous buffer, or in case of ill-defined or no inflection point, to the meter reading corresponding to the pH 11 aqueous buffer, mL. For additives, A is the volume of alcoholic KOH at the last inflection point,
B = volume corresponding to A for blank titration, mL,
M = concentration of alcoholic KOH solution, mol/L,
m = concentration of alcoholic HCl solution, mol/L,
W = sample, mass, g,
C = alcoholic KOH solution used to titrate the sample to end point that occurs at a meter reading corresponding to the pH 4 aqueous buffer, mL, and
D = alcoholic HCl solution used to titrate solvent blank to end point corresponding to C, mL.

