11. Report
11.1 Report the following information:
11.1.1 Grease identity,
11.1.2 Test date,
11.1.3 Test temperature and duration, and
11.1.4 Oil separation, nearest 0.1 %.
12. Precision and Bias
12.1 Precision - Eight cooperators tested eight greases for leakage in a cooperative program conducted in accordance with the design-of-experiments described in RR: D02-1007. All tests were run in duplicate. The total range of results were from 0.1 to 23.7 % leakage (see Table 1).
12.2 The precision of the percent oil separation as determined by this test method was obtained in accordance with guidelines currently accepted by Committee D-2 (computer program: D2PP, Calculation of Precision Data: Petroleum Test Methods).
12.3 The repeatability and reproducibility of the test method as determined by statistical examination of the interlaboratory results are as follows:
12.3.1 Repeatability - The difference between two test results, obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant specified operating conditions on identical test material would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty:

where:
M = mean of two determinations.
12.3.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results by two different operators working in different laboratories on identical test material would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the following values only in one case in twenty:
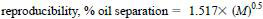
where
M = mean of two determinations.
12.4 Bias - The procedure for measuring the oil separation from lubricating grease has no bias because the value of the oil loss is defined only in terms of this test method.
13. Keywords
13.1 cone-bleed test; leakage; lubricating grease; oil bleed; oil separation



