13. Calculation
13.1 Screening - Aroclors are made up of numerous congeners and so the chromatograms are multi-peak. Often the chromatogram of the sample may not exactly match that of the standard due to factors such as environmental exposure, interferences not easily removed by cleanup techniques, and the presence of multiple Aroclors.
13.1.1 Visual determinations are made by comparing the chromatogram with the reference chromatograms. Set the data display conditions so that a 0.1 ug/mL standard is full scale on the chromatogram.
13.1.2 All samples in which an Aroclor is detected require a judgment concerning the amount. The recognized Aroclor pattern shall be compared to the IPS (0.01 ug/mL or 0.1 ug/mL). If the overall level of the suspected Aroclor pattern is equal to or greater than the overall level of the IPS pattern, then Tier II analysis may be used to quantitate the PCBs.
13.1.3 If Aroclor identification is prevented by the presence of interferences, additional sample preparation is required. All composites having such interferences shall be analyzed as individual samples. Individual samples may be diluted prior to analysis, but it must be remembered that the detection limit of the analysis has been changed. Used oil samples shall not be diluted beyond 1:100 during initial screening analysis to meet the regulated level of interest (2 ug/mL).
13.1.4 If PCBs are detected, (when compared to the IPS criteria above) the result is reported Positive. If no PCBs are detected above the IPS level, the result is Negative.
13.1.5 When screening for Aroclors, visual determination is made by the following key items:
13.1.5.1 Aroclor Pattern - The Aroclor pattern includes (a) Same singlets, doublets, and triplets present in the reference chromatograms, and (b) Same relative peak heights between peaks in the sample chromatogram and the reference chromatogram.
13.1.5.2 Retention times shall be very consistent between the standard and the sample peaks.
13.2 Data System Quantitation - The GC data system shall be calibrated for each Aroclor using a minimum of five peaks (with exception of Aroclor 1221, which uses three peaks) for each Aroclor. For use with integrators, divide the standard amount by the number of peaks being used (for example, using five peaks on a 0.5 ug/mL standard would assign 0.1 ug/mL to each peak.) For some data systems, the total standard amount may be assigned to each peak. This will allow for a calibration table to be made, yielding response factors for each peak.
NOTE 10 - Response factors are based on amount/area for some data systems, while response factors are based on area/amount for others.
13.2.1 Quantitation of Aroclor in samples requires selecting five peaks that are free of interferences (minimum of three peaks, if interferences present) in the TIER II analysis, and assigning the appropriate response factor to each peak.
13.2.2 Aroclors 1016/1260 are quantitated using a five point calibration. All other Aroclors use a single point calibration. Samples exceeding the working range shall be diluted prior to analysis so that quantitation is performed within the calibration range.
13.2.3 As an example, the data system shall be set up to provide results in ug/mL. The following equation yields the concentration of Aroclors in mg/kg on a wet weight basis.

After determining the water content, using Test Method E 203, the concentration of Aroclor in a sample is corrected for dry weight of the sample by the following:
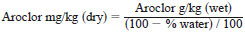
Water content is usually determined by Test Method E 203.
13.3 Manual Quantitation - Quantitate Aroclor samples by comparing the area of five sample peaks (minimum of three, if interferences present) to the area of the same peaks from appropriate (mid level) reference standards. Use only those peaks from the sample that are attributed to Aroclors. These peaks shall be present in the chromatogram of reference materials. See Aroclor Calculation Work Sheet (Appendix X2.) for an example of how to perform manual quantitation.
13.3.1 Use the following formulas to calculate the concentration of each of the Aroclor peaks in the sample (wet weight):
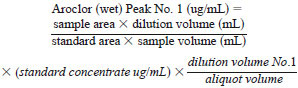
13.3.2 This is repeated for each peak used, and the results summed to give the wet concentration.
The result may be converted from ug/mL to ug/g by:
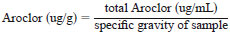
Specific gravity may be the measured value or calculated by (sample weight/3 mLs).
Care shall be taken in handling viscous samples as the volumes may not be correct. In those cases the measured sample weight shall be used.
A simplified formula using sample weight is:
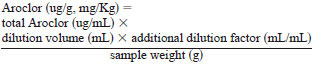
The concentration of Aroclor in a sample is corrected for dry weight of the sample by the following:
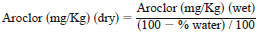
13.4 Mixed Aroclors - For routine Tier II samples showing evidence of mixed Aroclors, select a minimum of three peaks lacking significant interference for each identified Aroclor and quantitate. Report the amount for each Aroclor separately.
NOTE 11 - This approach will normally overstate the PCB concentration and, thus, is considered to be a conservative approach.
13.4.1 Since mixed Aroclors present special problems in quantitation, it is permissible to prepare individualized mixed standards in an attempt to match the suspected sample concentrations and obtain greatest possible accuracy. This will involve a judgment about what proportion of the different suspected Aroclors to combine to produce the appropriate reference material. A calibration standard is then made using this blend. Use only those peaks from the sample that are attributed to chlorobiphenyls. These peaks shall be present in the reference blend.



