12. Procedure
12.1 Compositing - It is common to analyze mixtures of multiple samples, called composites, if a large number of samples are analyzed. This approach is described in Annex A3.
12.2 Sample Preparation Procedure:
12.2.1 Liquid Samples - Accurately pipette 3.0 mL of sample into a tared 40 mL vial (fitted with a TFE-fluorocarbon-lined cap) and weight. If the results are calculated by weight accurately weigh the sample and record the weight. Spike this sample with 100 uL of decachlorobiphenyl surrogate working standard.
12.2.1.1 Add 27 mL acetone/hexane to the vial, producing a 1:10 dilution. Cap it and vortex vigorously for at least 30 s. If the sample is not completely miscible with acetone/hexane, add more acetone to reach a total of approximately 30 mL extract and vortex again. (Alternatively, place capped vial in sonic bath for 5 min.)
12.2.2 Solid, Semi-solids, Sludge Samples - Weigh accurately 3.0 g of sample into a 40 mL vial fitted with a TFE-fluorocarbon-lined cap. Spike this sample with 100 uL of decachlorobiphenyl surrogate working standard. Add 30 mL of acetone/hexane to the vial for a 1:10 dilution. Vortex for at least 30 s.
12.2.2.1 If the sample does not totally dissolve, vortex again or place capped vial in sonic bath for 5 min. This shall provide adequate contact whether or not any further dissolution occurs.
12.2.3 Matrix Spike and Matrix Spike Duplicate Samples - Add 1.0 mL of spiking solution to the sample just after the addition of the surrogate and prior to the addition of the acetone-hexane solvent.
12.2.4 Centrifuge - If sediment is visible, centrifuge the extract to separate out the sediment.
12.3 Sample Clean-up - Clean-up is not required for all samples; however, interference problems due to the presence of other chemical species may usually be addressed using the procedures found in Annex A4.
12.4 Gas Chromatographic Analysis Sequence - Samples are analyzed in a set referred to as an analysis sequence.
12.4.1 Tier 1–Screening:
12.4.1.1 Standards Sequence (initially and optionally with recalibrations) - (a) Aroclor 1016/1260, at selected IPS level (5 times) and (b) The following may be mixed as described below and shall be analyzed at 0.1 ug/mL each (for 20 mg/Kg level of interest use 0.2 ug/mL).
Aroclor: 1221
Aroclor: 1232
Aroclor: 1242
Aroclor: 1248
Aroclor: 1254
Aroclor: 1262
Aroclor: 1268
12.4.1.2 Some of the standards in 12.4.1.1 may be run as mixed standards:
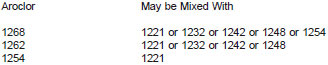
12.4.1.3 A Typical Analysis Sequence - A typical analysis sequence includes (a) reagent blank (optional), (b) Instrument Performance Standard (IPS) (every 20 samples or every day, whichever is more frequent), (c) method blank, and (d) Samples 1 to 20.
12.4.1.4 Repeat this sequence as long as the system meets the IPS criteria.
12.4.2 Tier 2 - Quantitation:
12.4.2.1 Standards Sequence - The standards sequence includes (a) reagent blank, (b) Aroclor 1016/1260 (5 point calibration), (c) Aroclor 1268 mid-level standard, (d) Mid level standard of suspected Aroclors if not, 1016 or 1260, and (e) (CCS, five times, to establish DCB response, if DCB is not spiked in 1016/1260 standards.)
12.4.2.2 A Typical Analysis Sequence - A typical analysis sequence includes (a) reagent blank (optional), (b) CCS (1016/1260 mid standard), (c) method blank, (d) Samples 1 to 20, (e) matrix spike sample, and (f) matrix spike duplicate.
12.4.2.3 Repeat this sequence as long as the system meets the quality assurance criteria.
12.5 Inject 2 uL of the sample extract into the gas chromatograph using an autosampler or a manual injection.
12.6 Set the data display (printer or video screen) conditions so that a mid point calibration standard shall be full scale on the chromatogram.
12.7 If the results exceed the calibrated range of the system, and quantitication is desired, the extract shall be diluted and reanalyzed within the calibration range.

