1. Scope
1.1 This test method is a two-tiered analytical approach to PCB screening and quantitation of liquid and solid wastes, such as oils, sludges, aqueous solutions, and other waste matrices.
1.2 Tier I is designed to screen samples rapidly for the presence of PCBs.
1.3 Tier II is used to determine the concentration of PCBs, typically in the range of from 2 to 50 mg/kg. PCB concentrations greater than 50 mg/kg are determined through analysis of sample dilutions.
1.4 This is a pattern recognition approach, which does not take into account individual congeners that might occur, such as in reaction by-products. This test method describes the use of Aroclors 1016, 1221, 1232, 1242, 1248, 1254, 1260, 1262, and 1268, as reference standards, but others could also be included. Aroclors 1016 and 1242 have similar capillary gas chromatography (GC) patterns. Interferences or weathering are especially problematic with Aroclors 1016, 1232, and 1242 and may make distinction between the three difficult.
NOTE 1 - Aroclor is a registered trademark of Monsanto.
1.5 This test method provides sample clean up and instrumental conditions necessary for the determination of Aroclors. Gas chromatography (GC) using capillary column separation technique and electron capture detector (ECD) are described. Other detectors, such as atomic emission detector (AED) and mass spectrometry (MS), may be used if sufficient performance (for example, sensitivity) is demonstrated. Further details about the use of GC and ECD are provided in Practices E 355, E 697, and E 1510.
1.6 Quantitative results are reported on the dry weights of waste samples.
1.7 Quantification limits will vary depending on the type of waste stream being analyzed.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulator limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 4059 Test Method for Analysis of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in Insulating Liquids by Gas Chromatography
E 203 Test Method for Water Using Karl Fischer Reagent
E 288 Specification for Laboratory Glass Volumetric Flasks
E 355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Relationships
E 697 Practice for Use of Electron-capture Detectors in Gas Chromatography
E 969 Specification for Glass Volumetric (Transfer) Pipet
E 1510 Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular Capillary Columns in Gas Chromatography
2.2 U.S. EPA Standards:
Method 608 Organochlorine Pesticides and PCBs Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory, Cincinnati, Ohio. EPA Report 600/4/82–057.
Method 680 Determination of Pesticides and PCBs in Water and Soil/Sediment by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
Method 3620 Florisil Column Clean-Up
Method 3630 Silica Gel Clean-Up
Method 3660 Sulfur Clean-Up
Method 8082 Determination of PCB in Water and Soil/Sediment by Gas Chromatography: Capillary Column Technique
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 Aroclors, n - commercial mixtures of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners marketed and trademarked by Monsanto prior to 1977.
3.1.1.1 Discussion - Specific Aroclors are usually designated by a four-digit number, with the first two digits usually designating the number of carbon atoms and the last two digits providing the chlorine content (for example, Aroclor 1260 is 60 % (weight) chlorine).
3.1.2 congeners, n - compounds related by structural similarities.
3.1.2.1 Discussion - All polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) share the same C12 structure and vary only by the number and position of the chlorine atoms attached to the aromatic rings.
3.1.3 continuing calibration standard (CCS) - a known blend or one or more Aroclors at a fixed concentration that is injected into the gas chromatograph to demonstrate the validity of the calibration.
3.1.4 dry weight, n - concentration of PCBs after factoring
out the water content.
3.1.4.1 Discussion - This correction assumes that all PCBs originated from nonaqueous sources and any water present has been added subsequently, diluting the original concentration. This correction can be described using the formula:
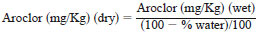
3.1.5 instrument performance standard (IPS), n - a known low level of an Aroclor in a clean solvent used as a comparator to determine which qualitative (screening) results are of sufficient magnitude to require quantitative analyses.
3.1.6 surrogate,n, n - compound or compounds that are similar to analytes of interest in chemical composition, extraction, and chroatography, but that are not normally found at significant levels in the matrices of interest.
3.1.6.1 Discussion - Surrogates may be spiked into blanks, standards, samples, or matrix spikes prior to analysis to allow a determination of a quantitative recovery rate. Surrogates are also used to document matrix effects and method control.
3.1.7 waste material, n - any matter, within the scope of this test method, that is in the process of being recycled or disposed.

