ASTM D6139 Standard Test Method for Determining the Aerobic Aquatic Biodegradation of Lubricants or Their Components Using the Gledhill Shake Flask
13. Calculation
13.1 The total organic carbon content of the test material (or reference material) determined by elemental analysis is used to calculate the theoretical quantity of CO2 evolution for each replicate as follows:
13.1.1 Test material (or reference material) contains a specific weight fraction of carbon, therefore:
Yi = w xTi
where:
Yi = carbon charged to the test medium in the ith replicate, mg,
w = weight fraction of carbon in test material expressed as a decimal, and
Ti = test material (or reference material) added to the test medium in the ith replicate, mg.
13.1.2 The theoretical amount of CO2 which could be produced if all of the carbon in the material is converted to CO2, is then calculated by knowing 12 g carbon yields 44 g CO2, therefore:
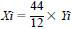
where:
Xi = theoretical amount of CO2, which could be produced from Yi, mg, and
Yi = carbon charged to the test medium in the ith replicate, mg.
13.2 Amount of CO2 Produced: (For the ith replicate flask for the test material (or reference material):
13.2.1 Calculate the amount of CO2 produced for a specific titration (Cxi) for the test material (or reference material) as follows:
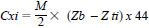
where:
Cxi = CO2 produced for a specific titration in the ith replicate, mg,
M = molarity of HCl,
Zb = HCl needed to titrate Ba(OH)2 solution for blank controls (the average HCl titration volume of the blank control replicates will be used), mL, and
Zti = mL of HCl needed to titrate Ba(OH)2 solution for test material (or reference material) for theith replicate.
This equation corrects for background CO2 from the blank control in which no test or reference material (that is, no additional carbon source) was added.
13.2.2 Calculate the total amount of CO2 (Cti) produced for the ith replicate for the test or reference material by summing the results obtained for each titration.
Cti = ∑Cxli . . . Cxni
From the Cti values for the replicates, determine the mean and standard deviation for the test material (or reference material).
13.2.3 Percent of theoretical CO2 evolved (Pi) for the ith replicate is calculated as shown below:
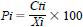
where:
Cti = total amount of CO2 calculated by summing the CO2 produced at each titration interval for a given test or reference material for the ith replicate, and
Xi = theoretical CO2 produced from a given material for the ith replicate, mg.
From the replicate values, determine the mean and standard deviation for percent of theoretical CO2 evolved for the test material (or reference material).

