ASTM D6130 Standard Test Method for Determination of Silicon and Other Elements in Engine Coolant by Inductively Coupled Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
12. Report
12.1 Samples prepared by weight to volume dilution may be reported in ppm by weight or % by weight depending on the concentration of the element of interest. Samples prepared by volume may be reported as g/L, mg/L, µg/mL, etc. These units may be converted to ppm weight or % by weight using the density of the sample:
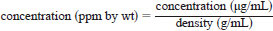
13. Precision and Bias
13.1 Precision - The precision of this test method for silicon was determined by statistical examination of interlaboratory results according to Practice E 691 is as follows:
13.1.1 Repeatability - The difference between successive test results obtained by the same operator on the same test material would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, be expected to be as indicated in Table 2. Average relative repeatability, that is, within laboratory consistency, is 6 %.
13.1.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results, obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test materials would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of this test method, be expected to be as indicated in Table 2. The relative reproducibility never exceeds twice the repeatability and on average is about 1-1/2 times, at 9 %, the repeatability.
NOTE 1 - Ten laboratories and six samples were involved in this interlaboratory study. Data from only seven laboratories are available.
13.2 Bias - Since there is no accepted reference material suitable for determining the bias for this test method, bias has not been determined.
14. Keywords
14.1 engine coolant; inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy; silicon

