ASTM D6078 Standard Test Method for Evaluating Lubricity of Diesel Fuels by the Scuffing Load Ball-on-Cylinder Lubricity Evaluator (SLBOCLE)
11. Procedure A, Incremental-Load Test
11.1 Install Cleaned Test Cylinder:
NOTE 3 - The SLBOCLE is very sensitive to contamination problems.
11.1.1 Adhere strictly to cleanliness requirements and to the specified cleaning procedures. During handling and installation procedures, protect cleaned test parts (cylinder, balls, reservoir, and reservoir cover) from contamination by wearing clean cotton gloves.
11.1.2 Secure the load beam in the UP position by inserting the load arm pull pin.
11.1.3 Push the drive shaft through the left-hand bearing and support bracket.
11.1.4 Hold the cylinder with the set screw hub facing left. Push the drive shaft through the cylinder bore, through the right-hand bearing support bracket, and into the coupling as far as the drive shaft will go.
11.1.5 Align the coupling set screw with the flat keyway side of the cylinder drive shaft. Tighten set screw.
11.2 Position Cylinder:
11.2.1 For a new cylinder, set the micrometer at 2.50 mm and slide cylinder to the left until it is firmly against micrometer probe. Ensure that cylinder set screw is directed toward the keyway (flat surface of drive shaft) and tighten set screw. This should position the first wear track on a ring approximately 1 mm in from the left side. If a cylinder used for a previous fuel is being used, then position the new wear track at least 0.75 mm to the right of the last track on the ring.
11.2.2 Back micrometer probe away from the cylinder before the drive motor is engaged.
11.2.3 Record on the data sheet the ring number, if assigned, and the position of the test cylinder as indicated by the micrometer. The first and last wear tracks on a ring shall be approximately 1 mm in from either side.
11.3 Install a clean test ball by first placing the ball in the retaining nut, followed by the retaining ring. Screw the retaining nut onto the threaded chuck located on the load arm and hand tighten.
11.4 Install the clean reservoir. Install the spacing platform by raising the reservoir. Slide the spacer platform into position under the reservoir. Place the thermocouple in the hole provided at the rear left side of the reservoir.
11.5 Supply test fluid in accordance with Practice D4306. Transfer 50 +/- 1 mL of the test fluid to the reservoir. Place the cleaned reservoir cover in position and attach the 1/4 to 1/8-in. air lines t the reservoir cover.
11.6 Move the power switch to the ON position.
11.7 Adjust the reservoir temperature, as required, until temperature stabilizes at 25 +/- 1°C. Adjust thermostat of the heat exchanger circulating bath to obtain the required temperature.
11.8 Turn on the compressed air cylinder. Adjust the delivery pressure to 350 kPa and the console air pressure to 200 kPa.
NOTE 4 - At loads above 4500 g, manual assist may be necessary.
11.9 Place lift actuator switch in the UP position.
11.10 Using the flowmeters that control the wet and dry airflows, adjust total airflow to read 3.8 L/min. Maintain 50 +/- 2 % relative humidity.
NOTE 5 - Fifty percent relative humidity requires approximately equal volumes of wet and dry air.
11.11 Set fuel aeration timer for 15 min and adjust fuel aeration flowmeter to 0.5 L/min.
11.12 At completion of aeration, the whistle will sound and aeration will cease. Continue 3.8 L/min flow through the reservoir.
11.13 Break-In:
11.13.1 Place the 500-g load on the load arm.
11.13.2 Remove the load arm pull pin and gently lower load arm until the complete load is supported by the pneumatic piston. Do not allow the ball specimen to contact the ring.
11.13.3 Start rotation of cylinder by switching motor drive to ON. Set rotation to 525 rpm.
11.13.4 Move actuator switch to DOWN position. The load arm will lower and the ball will contact the test ring. 11.13.4.1 The lift arm actuator valve on the side of the cabinet controls the rate at which the load arm lowers. The valve controls the bleed from the pneumatic lift cylinder. Adjust the valve so that the full load is applied to the ball and contact between the pneumatic lift cylinder and load arm ceases after 5 s.
11.13.5 Switch the timer on for 30 s.
11.13.6 When the whistle sounds at the end of 30 s, immediately remove the test load, manually raise the load arm and insert the load arm pull pin. do not rely on the pneumatic lift cylinder to life the load arm.
11.13.7 Place the lift actuator switch in the UP position.
11.14 Incremental-Loads:
11.14.1 Place 2800 g load on load arm.
11.14.2 Remove the load arm pull pin and gently lower the load arm until the complete load is supported by the pneumatic piston. Do not allow the ball specimen to contact the ring.
11.14.3 Start rotation of the the cylinder by switching motor drive to ON. Set rotation to 525 +/- 1 rpm.
11.14.4 Switch on the recording device for friction trace output.
11.14.5 Check all test condition readouts and adjust as necessary. Record all necessary information on the data sheet.
11.14.6 Move the actuator switch to the DOWN position. The load arm will lower and the ball will contact the ring.
11.14.7 Switch the timer on for 60 s.
11.14.8 When the whistle sounds at the end of 60 s, immediately remove the test load, manually raise the load arm, and insert the load arm pull pin. Do not rely on the pneumatic lift cylinder to lift the load arm. If severe vibration or severe changes in sounds are evident, terminate the test prior to completion of the 60 s.
11.14.9 Place the lift actuator switch in the UP position.
11.14.10 Turn the motor drive switch to the off and switch off recording device. Manually rotate motor shaft and wipe the revolving ring with an UNUSED disposable, lint-free cloth to remove residue from the test ring.
11.14.11 Remove the test ball from the locking nut. Wipe the ball clean with a disposable wipe. Replace with a new ball as described in 11.3.
11.14.12 Calculate the MAXIMUM friction coefficient as described in Section 14 Typical plots of friction coefficient versus time, where the maximum friction coefficient does and does not exceed 0.175, are shown in Fig. 4.
11.14.13 Loosen the coupling set screw, NOT the mandrel set screw, and reset the cylinder to a new test position at least 0.75 mm from the last track by adjusting the micrometer. The reservoir cover is not removed to loosen the mandrel set screw after the initial aeration is completed to minimize atmospheric contamination between tests.
11.14.14 The maximum number of loads per ring is 15.
11.14.15 Based on the maximum friction coefficient and Fig. 5, choose the next load increment and repeat the testing sequence from 11.13 through 11.14.13 except for substituting the new load for the 2800 g load in 11.14.1.
11.14.16 Terminate the incremental-load tests when the applied load for a maximum friction coefficient exceeding and not exceeding 0.175 differs by 100 g.
11.14.17 Repeat the test procedure from 11.1 with a different, precleaned test ring to verify the initial result. This does not constitute a duplicate result because a new sample of the fuel has not been used.
11.14.17.1 Do NOT replace or aerate the test fluid unless the total number of test increments performed with that fluid exceeds twelve.
11.14.17.2 For the repeat test procedure, more rapid covergence may be obtained by using load increments near to the previously obtained result.
11.14.17.3 If the two test results differ by 500 g, or more, the results are not reliable and should be discarded. The complete test procedure detailed in Section 10 should be repeated until two test results are within 500 g.
12. Procedure B, Single-Load Test
12.1 If one selects an applied load which is considered to represent a minimum acceptable level, that is, a level at which no scuffing should be observed, then a single-load test can be conducted at this applied load.
12.2 Prepare, calibrate, and standardize the equipment as described in Sections 9 and 10.
12.3 Follow the procedure given in 11.1 through 11.13.7.
12.4 Place the selected load on the load arm.
12.5 Follow the procedure given in 11.14.2 through 11.14.12
12.6 If the maximum friction coefficient from 11.14.12 is less than or equal to 0.175, the fuel is considered to have passed at the selected load.
12.7 If the maximum friction coefficient from 11.14.12 is greater than 0.175, the fuel is considered to have failed due to scuffing at the selected load.
13. Measurement of Friction
13.1 Friction Measurement - Read and record the maximum tangential friction force in grams from the friction trace recording.
14. Calculation
14.1 Calculate the maximum friction coefficient as follows:
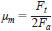
where:
µm = maximum friction coefficient,
Ft = maximum tangential friction force, g, from friction trace recording, and
Fa = applied load, g.



