ASTM D6069 Standard Test Method for Trace Nitrogen in Aromatic Hydrocarbons by Oxidative Combustion and Reduced Pressure Chemiluminescence Detection
7. Apparatus
7.1 Pyrolysis Furnace - A furnace capable of maintaining a temperature sufficient to volatilize and pyrolyze the sample and oxidize organically bound nitrogen to NO. The actual temperature(s) should be recommended by the specific instrument manufacturers.
7.2 Quartz Pyrolysis Tube - Capable of withstanding 900 to 1200°C.
7.2.1 Quartz Pyrolysis Tube - The suggested maximum temperature for a quartz pyrolysis tube is 1200°C. Samples containing alkali-metals (elements from the Periodic Group IA (that is, Na, K, etc.)) or alkaline earths (elements from the Periodic Group IIA (that is, Ca, Mg, etc.)) will cause quartz to devitrify (that is, become milky white and brittle).
7.3 Chemiluminescent Detector - Capable of operation at reduced pressures (less than 760 mm mercury) and able to measure light emitted from the reaction between NO and ozone. Includes ozone generator.
7.4 Microlitre Syringe - Capable of delivering from 5 to 50 µL of sample. Check with the instrument manufacturer for recommendations for specific sample needs.
7.5 Constant Rate Injector System (Optional) - If the sample is to be introduced into the pyrolysis furnace via syringe, a constant rate injector should be used.
7.6 Boat Inlet System (Optional) - If the instrument is equipped with a boat inlet system, care must be taken to ensure the boat is sufficiently cooled between analyses to prevent the sample from vaporizing as it is injected into the boat. The sample should start vaporizing as it enters the furnace. It is critical that the sample vaporize at a constant and reproducible rate. This type of inlet system offers advantage when the sample is viscous or contains heavy components not volatile at temperatures of approximately 300°C, or for samples that contain polymers or high concentrations of salts that could result in plugging of the syringe needle.
7.7 Automatic Boat Drive System (Optional) - If the instrument is equipped with a boat inlet system, a device for driving the boat in to the furnace at a controlled and repeatable rate may improve data repeatability and reproducibility.
7.8 Oxidation Catalyst (Optional) - Catalyst (that is, cupric oxide (CuO) or Platinum (Pt)) may be packed into the pyrolysis tube to aid in oxidation efficiencies (see manufacturer's recommendations).
8. Reagents
8.1 Purity of Reagents - Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests. It is intended that all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where such specifications are available, unless otherwise indicated. Other grades may be used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of the determination.
8.2 Inert Gas - Either argon (Ar) or helium (He) may be used. The purity should be no less than 99.99 mol %.
8.3 Oxygen Gas - The purity should be no less than 99.99 mol %.
8.4 Solvent - The solvent chosen should be capable of dissolving the nitrogen containing compound used to prepare the standard and if necessary the samples. The solvent of choice should have a boiling point similar to the samples being analyzed and it should contain less nitrogen than the lowest sample to be analyzed. Suggested possibilities include, but are not limited to: toluene, methanol, tetrahydrofuran, iso-octane.
NOTE 2 - A quick screening can be conducted by injecting the solvent and sample once or twice and comparing relative area counts.
8.4.1 Solvent - Toluene, relative density at 60°F/60°F 0.8718 (see Test Method D1555).
8.5 Nitrogen Stock Solution, 1000 µg N/mL - Prepare a stock solution by accurately weighing, to the nearest 0.1 mg, approximately 707.7 mg of 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP) (CAS No. 872-50-4) into a 100-mL volumetric flask. Fill to volume with solvent as follows:
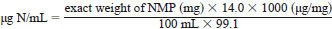
where:
14.0 = the atomic weight of nitrogen, and
99.1 = the molecular weight of NMP.
8.6 Nitrogen Working Standard Solutions, 1.0 and 2.0 µg N/mL - The working standards are prepared by dilution of the stock solution with the solvent. Prepare a 100-µg N/mL standard by accurately pipetting 10 mL of stock solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask and diluting to volume with solvent. This standard is further diluted to 1.0 and 2.0-µg N/mL by accurately pipetting 1 mL of the 100 µg-N/mL standard into a clean 100-mL volumetric flask and pipetting 2 mL of the 100-µg N/mL standard into a different clean 100-mL volumetric flask and diluting each to volume with solvent.
NOTE 3 - Working standards should be prepared on a regular basis depending upon the frequency of use and age. Typically, standards have a useful life of about 3 months.
8.7 Cupric Oxide (CuO) or Platinum (Pt) - May be used as an oxidation catalyst, as recommended by the instrument manufacturer.
8.8 Quartz Wool - May be needed if recommended by the instrument manufacturer.



