ASTM D5974 Standard Test Methods for Fatty and Rosin Acids in Tall Oil Fractionation Products by Capillary Gas Chromatography
INTERNAL STANDARD METHOD
7. Apparatus
7.1 Gas Chromatograph - An instrument equipped with a flame ionization detector (FID) that can be operated at conditions given in 10.1.
7.2 Column - A high resolution column between 15 and 60 m in length, 0.25 to 0.53 mm internal diameter, with a 0.20-µm film thickness of biscyanopropylsiloxane type liquid phase.
The recommended referee column is 30 m in length, 0.32 mm internal diameter, with a 0.20-µm film thickness, and provides separations equivalent or better than that displayed in Fig. 1.
NOTE 4 - When using this method for referee purposes, verify that the resolution is adequate and comparable to that shown in Fig. 1.
7.3 Analytical Balance, accurate to 0.1 mg.
8. Reagents and Materials
8.1 Purity of Reagents, see 4.2.1.
8.2 Myristic Acid (Internal Standard), 99 % pure.
NOTE 5 - A higher molecular-weight saturated fatty acid that elutes as a methyl ester later in the chromatogram may be used in place of, or in addition to myristic acid, provided that the alternative internal standard peak does not coelute with sample component peaks.
8.3 Stearic Acid, Oleic Acid, Linoleic Acid, Abietic Acid, and Dehydroabietic Acid - Other high purity reference standards can be added as needed.
9. Procedure
9.1 Preparation of Calibration Standard:
9.1.1 Accurately weigh into a suitable vial, milligram quantities of the myristic acid internal standard, plus the fatty acid and rosin acid standards that are anticipated to be in the test sample, and record the weights.
9.1.2 Convert the calibration standard to the methyl esters or substituted ammonium salts as described in Sections 4, 5, 6.
9.2 Preparation of Test Sample:
9.2.1 Accurately weigh ~50 mg of sample and ~15 mg of myristic acid directly into a suitable vial and record the weight.
NOTE 6 - Rosin samples need to be freshly broken from a larger mass to ensure the results are not affected by air oxidation of the rosin.
9.2.2 Convert the test sample to methyl esters or substituted ammonium salts, as described in Sections 4, 5, 6.
10. Set-up of Gas Chromatograph (GC)
10.1 Set the GC conditions so that they are approximately (see Note 7) as follows:

NOTE 7 - These are typical operating conditions only. The individual instrument should be adjusted in accordance with manufacturer's instructions to optimize desired performance. Ongoing adjustments in operating temperature and flow rate may be necessary to maintain optimum performance of the column due to aging.
10.2 Calibration:
10.2.1 Inject 0.5 to 1.0 µL of the appropriate standard prepared in 9.1.
10.2.2 Record the retention time and calculate the individual relative response factors as follows:
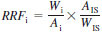
RRFI = relative response factor of individual fatty or rosin acid methyl esters,
WI = weight of individual fatty or rosin acid methyl esters in standard, Wi = weight used x purity,
AI = peak area of individual fatty or rosin acid,
AIS = peak area of internal standard, and
WIS = weight of internal standard. WIS = weight used x purity.
NOTE 8 - For highest accuracy, the purity of the standards should be used to correct the weight terms.
11. Analysis
11.1 Inject 0.5 to 1.0 µL of the test sample prepared in 9.2.2.
NOTE 9 - Dilution of the sample with additional solvent may be necessary to obtain injections that do not overload the column or detector.
12. Calculation
12.1 Obtain the peak areas of all of the peaks needed from the chromatogram.
NOTE 10 - See Fig. 1 for chromatogram of a typical distilled tall oil (DTO).
12.2 Calculate the absolute value of each peak of interest, as follows:
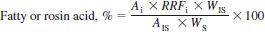
AI = peak area for fatty or resin acid methyl ester being determined,
RRFI = relative response factor for individual compound being determined,
WIS = weight of internal standard. WIS = weight used times purity,
AIS = peak area of internal standard, and
WS = sample weight.
13. Report
13.1 Report the percentage of the individual fatty and rosin acids to the nearest 0.1 %.
14. Precision and Bias
14.1 Internal Standard Method - An interlaboratory study of the capillary GC determination of fatty and rosin acids in tall oil fatty acids (TOFA), DTO, and rosin was run in 1995 by nine laboratories. The design of the experiment, similar to that of Practice E691, and a within-between analysis of the data are given in ASTM Research Report.
14.1.1 Test Result - The precision information given in Table 1 for fatty and rosin acids is for the comparison of two test results.
NOTE 11 - Repeatability = within laboratory, Reproducibility = between laboratories.
14.1.2 Bias - Since there is no accepted reference material, method or laboratory suitable for determining the bias for the procedure in this test method for measuring component concentration, no statement on bias is being made.



