ASTM D5623 standard test method for sulfur compounds in light petroleum liquids by gas chromatography and sulfur selective detection
9. Procedure
9.1 A list of typical apparatus and conditions is provided in 5.2.1. Table 2 provides a listing of the retention times for common sulfur compounds that are typical for the column and conditions specified in 5.2.1. Whenever possible, the retention times of sulfur compounds of interest should be determined experimentally. Fig. 1 shows a chromatogram from a typical analysis.
9.2 Sample Preparation for Analysis by Internal Standardization - Add a quantity of suitable internal standard dissolved in iso-octane or another suitable solvent (internal standard stock solution, 6.1.6.1), to an accurately measured quantity of sample on a gravimetric (mass) basis. The final concentration of the internal standard in the sample aliquot, on a sulfur basis, should be approximately one half of the concentration range of sulfur compounds in the original sample. A concentration of approximately 1 to 50 mg/kg of internal standard on a sulfur basis has been used successfully for most samples.
9.3 Sample Analysis by External Standardization - At least once a day, or as frequently as deemed expedient, use the external standard(s) (6.1.5) to calibrate the instrument. The volume of external standard injected for calibration must be exactly the same as the sample volume injected for analysis.
9.4 Chromatographic Analysis - Introduce a representative aliquot of sample into the gas chromatograph. For internal standardization, the sample aliquot must contain a measured quantity of internal standard (6.1.6). Exercise care that the amount of sample and standard injected does not cause detector saturation (indicated by flat-topped peaks). Typical sample size ranges from 0.1 to 2.0-µL. Obtain the chromatographic data by way of a potentiometric recorder (graphic), digital integrator, or computer based chromatographic data system. Examine the graphic display or digital data for any errors.
10. Calculations
10.1 Mass Concentration of Sulfur Compounds as Sulfur - After identifying the sulfur compounds of interest by retention time, measure the area of each sulfur peak.
10.1.1 Sulfur Concentration by Internal Standardization - Compare the area response of each sulfur compound of interest to that of the internal standard. Calculate the concentration of each sulfur peak according to Eq 2:
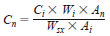
where:
Cn = concentration (mg/kg) of sulfur compound as sulfur,
Ci = concentration (mg/kg) of internal standard in stock solution calculated as sulfur,
Wi = mass of internal standard stock solution added to the sample,
An = peak area of the sulfur compound,
Wsx = mass of sample aliquot, and
Ai = peak area of the internal standard.
10.1.2 Sulfur Concentration by External
Standardization - An appropriate external standard (6.1.5) is chosen for calibration. The sulfur compound(s) and matrix of the external standard chosen should be representative of the sample(s) being analyzed. Compare the area response of each sulfur compound of interest to that of the external standard. Calibrate the concentration of each sulfur peak according to Eq 3:
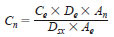
where:
Cn = concentration (mg/kg) of sulfur compound as sulfur,
Ce = concentration (mg/kg) of external standard calculated as sulfur,
De = density of external standard matrix,
An = peak area of the sulfur compound,
Dsx = density of sample matrix, and
Ae = peak area of the external standard.
This equation assumes that equivalent volumes of sample and standard are injected.
10.2 Report the concentration of each sulfur compound as sulfur in units of mg/kg (ppm wt) to the appropriate number of significant figures.
10.3 Mass Concentration of Total Sulfur in Sample - Sum the sulfur content of all sulfur components (known and unknown) in the sample to arrive at its total sulfur value according to Eq 4:
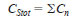
where:
CStot = concentration of total sulfur in the sample.
10.4 Report the concentration of total sulfur in units of mg/kg to the appropriate number of significant figures.
10.5 Mass Concentration of Sulfur Compounds as Compound - In 9.1 the concentration of sulfur compounds is reported on a sulfur basis. In some instances the concentration of sulfur compounds as compound is of interest. This conversion is made according to Eq 5:
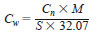
where:
Cw = concentration of the sulfur compound as compound,
Cn = concentration of sulfur compound as sulfur,
M = Molar mass of the compound in g/mol,
S = number of sulfur atoms in the molecular formula of the compound, and,
32.07 = the mass of one mol of sulfur, g.

