ASTM D5599 Standard Test Method for Determination of Oxygenates in Gasoline by Gas Chromatography and Oxygen Selective Flame Ionization Detection
11. Procedure
11.1 Keep samples refrigerated until ready for analysis. Bring samples to room temperature prior to analysis.
11.2 Tare the sample container and its rubber-faced PTFE-faced sealing cap. Transfer 1 to 10 g of the sample to the container and seal immediately. Weigh the sample container and contents to the nearest 0.1 mg and record the mass of test sample.
11.3 Tare the sample container and contents, then inject through the rubber membrane a volume of the same internal standard used in generatingstandards. Record themass of internal standard added to the nearest 0.1 mg. The mass of internal standard should be 2 to 6 % of the test sample but not less than 50 mg.
11.4 Ensure that the sample (gasoline plus internal standard) is thoroughly mixed. Transfer an aliquot of the solution to a vial compatible with the autosampler if such equipment is used. Seal the vial with a PTFE-lined septum cap.
11.5 Inject a suitable quantity (0.1 to 1.0 µL) of the sample containing internal standard into the chromatograph using the same technique and sample size as used for the calibration standards. The test portion size should be such as not to exceed the capacity of the column or linearity of the detector.
11.6 Acquire peak area and retention time data by way of electronic integrator or computer and, if desired, also by chart recorder.
12. Calculation and Report
12.1 Calculate the mass % of each calibrated oxygenate as follows:
12.1.1 After identifying the various oxygenates by retention times, obtain the areas of all calibrated oxygenate peaks and that of the internal standard. Calculate the area response ratio (rsp s) for each of the oxygenates using Eq 3 (10.3.1).
12.1.2 Calculate the amount ratio ( amts) for each calibrated oxygenate in the gasoline sample, by substituting that oxygenate's response ratio (rsps) and the coefficient of its quadratic calibration curve into Eq 5 (10.3.1) and solving.
12.1.3 Apply Eq 8 6 to determine the mass % of each calibrated oxygenate.
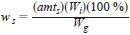
where:
ws = mass % of oxygenate in gasoline sample,
amts = amount ratio of oxygenate as determined in 12.1.2,
Wi = mass of internal standard added to gasoline sample, g, and
Wg = mass of gasoline sample, g.
12.1.4 If the mass % of any oxygenate exceeds its calibrated range, gravimetrically dilute a portion of the original sample with oxygenate-free gasoline to a concentration within the calibrated range and analyze the diluted sample in accordance with Section 11 and 12.1. Correct all mass % oxygenate values by multiplying by the dilution factor.
12.2 Calculate the total MTBE-equivalent mass % of uncalibrated oxygenates as follows:
12.2.1 Sum the peak areas of the uncalibrated oxygenates that are present. Do not include the peak areas due to dissolved oxygen, water, and the internal standard. Calculate the response ratio (rsps) for the summed areas of the uncalibrated oxygenates using Eq 3 (10.3.1).
12.2.2 Calculate the amount ratio ( amts) for the uncalibrated oxygenates in the gasoline sample by substituting the response ratio (determined in 12.2.1) and the coefficients of the MTBE calibration curve into Eq 5 (10.3.1) and solving.
12.2.3 Apply Eq 6 (12.1.3) to determine the total MTBE-equivalent mass % of the uncalibrated oxygenates.
12.3 Calculate the total mass % oxygen in the gasoline sample as follows:
12.3.1 Convert the mass % oxygenate of each individual, calibrated oxygenate to mass % oxygen and sum according to the following equation:
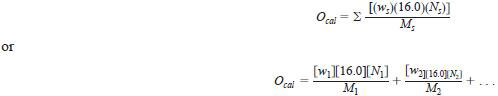
where:
Ocal = total mass percent oxygen from the calibrated oxygenates,
ws = mass % of each oxygenate as determined using Eq 6,
Ns = number of oxygen atoms in the oxygenate molecule,
Ms = molecular mass of the oxygenate as given in Table 2, and
16.0 = atomic mass of oxygen.
12.3.2 Convert the total MTBE-equivalent mass % of uncalibrated oxygenates to mass % oxygen according to the following equation:
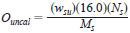
where:
Ouncal = total mass % oxygen from the uncalibrated oxygenates,
Wsu = MTBE-equivalent mass % of uncalibrated oxygenates,
Ns = number or oxygen atoms in MTBE molecule,
Ms = molecular mass of MTBE as given in Table 2, and
16.0 = atomic mass of oxygen.
12.3.3 Calculate the total mass % oxygen in the gasoline sample by summing the contributions from the calibrated components and the uncalibrated components.
Otot = Ocal + Ouncal
12.4 Report the mass % oxygenate of each calibrated oxygenate to the nearest 0.01 %. Also report the total mass % oxygen in the gasoline sample to the nearest 0.1 %.

