11. Gas Chromatographic Analysis Procedure
11.1 Set the instrument operating variables to the values specified in Table 1.
11.2 Set instrumental sensitivity such that any component of at least 0.002 mass % can be detected and integrated.
11.3 Inject 0.1 to 0.5 µL of sample into the injection port and start the analysis. Obtain a chromatogram and peak integration report. A sample chromatogram is shown in Fig. 1.
11.4 The ethanol peak will require tangential skimming to be correctly integrated if components of the denaturant elute on the ethanol peaks tail.
12. Calculation
12.1 Multiply the area of each identified peak by the appropriate mass relative response factor. Use those factors determined for individual compounds and use a factor of 1.000 for unknowns.
12.2 Determine the relative mass percent of the individual alcohols by using the following equation:
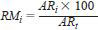
where:
RMi = relative mass % of the individual alcohols,
ARi = area of the individual alcohol peak corrected by the appropriate mass relative response factor (see 12.1), and
ARt = total area of all detected peaks corrected by their appropriate mass relative response factors (12.1 ).
12.3 Obtain the mass % of water in the sample. Test Methods D1364, E 1064, or equivalent, can be used.
12.4 Determine the mass % of the alcohols of interest by using the following equation:
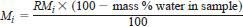
where:
Mi = mass % of the individual alcohol being determined, and
RMi = relative mass % of the individual alcohol from Eq 2.
12.5 For the volumetric concentration of the alcohol, calculate as follows:
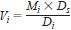
where:
Vi = volume % of component i,
Mi = mass % of component i from Eq 3,
Di = relative density at 15.56°C (60°F) of component i as found in Table 2, and
Ds = sample under study as determined by Test Method D1298 or D4052.



