ASTM D5453 Standard Test Method for Determination of Total Sulfur in Light Hydrocarbons, Motor Fuels and Motor Oils by Ultraviolet Fluorescence
11. Procedure
11.1 Obtain a test specimen using the procedure described in Section 8. The sulfur concentration in the test specimen must be less than the concentration of the highest standard and greater than the concentration of the lowest standard used in the calibration. If required, a dilution can be performed on either a weight or volume basis.
11.1.1 Gravimetric Dilution (mass/mass) - Record the mass of the test specimen and the total mass of the test specimen and solvent.
11.1.2 Volumetric Dilution (mass/volume) - Record the mass of the test specimen and the total volume of the test specimen and solvent.
11.2 Measure the response for the test specimen solution using one of the procedures described in 10.2-10.4.
11.3 Inspect the combustion tube and other flow path components to verify complete oxidation of the test specimen.
11.3.1 Direct Inject Systems - Reduce the sample size or the rate of injection, or both, of the specimen into the furnace if coke or sooting is observed.
11.3.2 Boat Inlet Systems - Increase the residence time for the boat in the furnace if coke or soot is observed on the boat. Decrease the boat drive introduction rate or specimen sample size, or both, if coke or soot is observed on the exit end of the combustion tube.
11.3.3 Cleaning and Recalibration - Clean any coked or sooted parts per manufacturer's instructions. After any cleaning or adjustment, assemble and leak check the apparatus. Repeat instrument calibration prior to reanalysis of the test specimen.
11.4 To obtain one result, measure each test specimen solution three times and calculate the average detector responses.
11.5 Density values needed for calculations are to be measured using Test Methods D1298, D4052, or equivalent, at the temperature at which the sample was tested.
12. Calculation
12.1 For analyzers calibrated using a standard curve, calculate the sulfur content of the test specimen in parts per million (ppm) as follows:
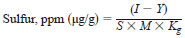
or
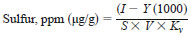
where:
D = density of test specimen solution, g/mL,
I = average of integrated detector response for test specimen solution, counts,
Kg = gravimetric dilution factor, mass of test specimen/mass of test specimen and solvent, g/g,
Kv = volumetric dilution factor, mass of test specimen/volume of test specimen and solvent, g/mL,
M = mass of test specimen solution injected, either measured directly or calculated from measured volume injected and density, V x D, g,
S = slope of standard curve, counts/µg S,
V = volume of test specimen solution injected, either measured directly or calculated from measured mass injected and density, M/D, µL, and
Y = y-intercept of standard curve, counts,
1000 = factor to convert µL to mL.
12.2 For analyzers calibrated using self calibration routine with blank correction, calculate the sulfur in the test specimen in parts per million (ppm) as follows:
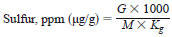
or
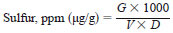
where:
D = density of test specimen solution, mg/µL (neat injection), or concentration of solution, mg/µL (volumetric dilute injection),
Kg = gravimetric dilution factor, mass of test specimen/mass of test specimen and solvent, g/g,
M = mass of test specimen solution injected, either measured directly or calculated from measured volume injected and density, V x D, mg,
V = volume of test specimen solution injected, either measured directly or calculated from measured mass injected and density, M/D, µL,
G = sulfur found in test specimen, µg, and
1000 = factor to convert µg/mg to µg/g.



