9. Interpretation of Results
9.1 Calculations are not required when prepackaged kits are used.
9.2 For Method A, report results as either greater than or less than 1000 mg/kg (ppm).
9.3 For Method B, calculate the concentration (mg/kg) of total chlorine in the original oil sample by the following equation:
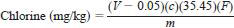
where:
V = volume of mercuric nitrate titrant used, mL,
0.05 = volume of excess titrant required for color formation, mL,
c = concentration of mercuric nitrate solution, meq/L, for example, 27.4,
35.45 = average atomic weight of chlorine,
F = dilution factor due to adding 7 mL of buffer solution and extracting only 5 mL for analysis, for example, 1.4, and
m = mass of oil sample used, for example, 0.34 g for a volume of 0.4 mL motor oil, g.
10. Quality Control
10.1 Test each sample two times. For Method A, if the results do not agree, a third test must be performed. Report the results of the two that agree. For Method B, the two results should be within 20 % or 300 mg/kg (whichever is larger) of each other. If they are not, perform a third test and report the results of the two tests that agree.
11. Precision and Bias
11.1 For Method A, no formal statement is made about
either the precision or bias of the test method because the result merely states whether there is conformance to the criteria for success specified in the procedure, that is, a blue or yellow color in the final solution. In a collaborative study, ten laboratories analyzed seven used oil samples and one unused motor oil sample using prepackaged test kits. Each laboratory ran each sample in duplicate. Out of the eighty samples that were run, one laboratory’s results disagreed with the rest of the laboratories' results on one sample. All 79 other tests were in agreement with their duplicates and with other laboratories' results. These data indicate that all participants get results of <1000 for all samples containing less than 870 mg/kg Cl, 9 out of 10 get >1000 on a sample at 1180 mg/kg, and all participants get >1000 at and above 1272 mg/kg. These data indicate that this test method makes correct predictions for samples containing <870 or >1272 mg/kg and probably correct predictions for samples between 870 and 1272 mg/kg Cl. See Table 1.
11.2 Precision and Bias Statement for Method B.
11.2.1 Precision - The following criteria should be used for judging the acceptability of results.
11.2.2 Repeatability - The difference between successive test results obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test material would, in the long run, and in the normal and correct operation of this test method, exceed the stated values only in one case in twenty.
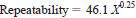
where:
X = method result, mg/kg.
11.2.3 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test material would, in the long run, and in the normal and correct operation of this test method, exceed the stated values only in one case in twenty.
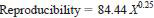
where:
X = method result, mg/kg.
11.2.4 In a collaborative study, using prepackaged kits, ten laboratories analyzed seven used oil samples and one unused motor oil sample.
11.2.5 Bias - No bias statement is made for this test method because results obtained for total chlorine were determined only by the test method itself.
12. Keywords
12.1 chlorine; field test; halogen; on-site testing; test kit; used oil

