ASTM D5186 Standard Test Method for Determination of the Aromatic Content and Polynuclear Aromatic Content of Diesel Fuels and Aviation Turbine Fuels By Supercritical Fluid Chromatography
9. Procedure
9.1 Using the same conditions as determined and used in Section 8, analyze the samples. Record the chromatographic data, stopping only when the sample has been completely eluted from the column. This is observed, at the end of the run, by the detector signal returning to baseline and remaining there. This will generally occur after the elution of the tricyclic aromatics.
9.2 Integrate the total chromatographic area from the beginning of the first peak to the return to baseline at the end of the chromatogram (see Fig. 1).
9.2.1 The chromatogram consists of one peak for the nonaromatics and one or more peaks for the aromatics.
9.2.1.1 Assign the area corresponding to the first peak (terminating at the bottom of the lowest valley between the retention times of hexadecane and toluene from the analysis of the performance mix) to the nonaromatics.
9.2.1.2 All of the integrated area eluting after the bottom of this valley but prior to the time corresponding to the start (not the apex) of the napthalene peak (determined in the analysis of the performance mixture) is assigned to the monoaromatics. Use area summing to determine the total area of this region in the chromatogram.
9.2.1.3 All of the integrated area occurring after the start time of the naphthalene peak through the final return to baseline is assigned to the polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons. Use area summing to determine the total area of this region in the chromatogram.
10. Calculation
10.1 Determine the mass % for monoaromatics, polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, and total aromatics content as follows:
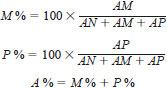
where:
M % = monoaromatics in sample, mass %,
P % = polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in sample, mass %,
A % = total aromatics in sample, mass %,
AM = area of monoaromatics in sample,
AN = area of nonaromatics in sample, and
AP = area of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons in sample.
11. Determination of Accuracy and Precision
11.1 Routinely assess the precision and accuracy of the analytical system as follows:
11.1.1 Accuracy - Analyze a check standard monthly as described in Section 9. The results obtained for total aromatics and polynuclear aromatics shall agree within the accepted reference values. Alternatively, exchange samples circulated as part of an interlaboratory program can be used as described in Section 6 on Reference Materials in Practice D6299. In this case, the analysis obtained shall not exceed the reproducibility limits given in Tables 3 and 4. Failure to attain the conditions described shall be followed by corrective action and subsequent verification of the accuracy assessment, prior to the analysis of samples.
11.1.2 Precision - At least once in a 24-h period, when performing the test method, analyze successively in duplicate a typical sample selected as a quality control (QC) sample as described in Section 6 on Reference Materials in Practice D6299. The sample is subjected to the procedures of Section 9. The results shall not exceed the repeatability values described in 13.1.1. Failure to achieve precision shall lead to corrective action and subsequent reevaluation of the precision. The record keeping of the analysis of this sample over time can be used to determine if the analytical system is under statistical control as described in Annex A1 on Statistical Quality Control Tools in Practice D6299.

