ASTM D5134 Standard Test Method for Detailed Analysis of Petroleum Naphthas through n-Nonane by Capillary Gas Chromatography
11. Split Injection Linearity
11.1 The choice of split ratio used is dependent upon the split linearity characteristics of the particular injector and the sample capacity of the column. Overloading of the column may cause loss of resolution for some components and, since overloaded peaks are skewed, variance in retention times. This can lead to erroneous component identification. During column evaluations and split linearity studies, watch for any skewed peaks that may indicate overload. Note the component size and where possible, avoid conditions leading to this problem during actual analyses.
11.2 Splitting injector linearity should be established to determine proper quantitative parameters and limits. Use a standard mixture of known weight percentages of 10 to 20 pure (99 + %) hydrocarbons, covering the boiling range of this test method. To prevent losses due to volatility, do not use any compounds lighter than n-hexane.
11.3 Inject and integrate this standard under the following conditions, using the operating conditions listed in Table 2. Split ratio may be determined by direct flow measurements or by calculation as shown in Annex A2. Faster temperature programming may be used as long as the components are eluted as discrete peaks.
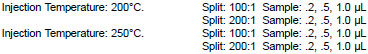
11.4 Calculate the concentration of each compound in the mixture by area normalization with response factors. Use a response factor of 1.00 for all compounds except benzene (0.90) and toluene (0.95). Determine the relative error of the calculated concentrations from the known concentrations.

11.5 Use only those combinations of conditions from 11.3 which result in 3 % or less relative error. This is the splitter linearity range.

