ASTM D5134 Standard Test Method for Detailed Analysis of Petroleum Naphthas through n-Nonane by Capillary Gas Chromatography
6. Apparatus
6.1 lnstrumentation - A gas chromatograph capable of column oven temperature programming from 35°C to 200°C in 1°C/min increments is required. A heated flash vaporizing injector designed to provide a linear sample split injection (for example, 200:1) is also required for proper sample introduction. The associated carrier gas controls must be of adequate precision to provide reproducible column flows and split ratios in order to maintain analytical integrity. A hydrogen flame ionization detector designed for optimum response with capillary columns (with the required gas controls and electronics) must meet or exceed the following specifications:
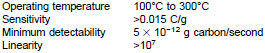
6.2 Sample Introduction System - Manual or automatic liquid syringe sample injection to the splitting injector may be employed. Devices capable of 0.2 µL to 1.0 µL injections are suitable. It should be noted that inadequate splitter design or poor injection technique, or both, can result in sample fractionation. Operating conditions which preclude fractionation should be determined in accordance with Section 11.
6.3 Electronic Data Acquisition System - Any data acquisition and integration device used for quantitation of these analyses must meet or exceed these minimum requirements:
6.3.1 Capacity for at least 250 peaks/analysis.
6.3.2 Normalized area percent calculation with response factors.
6.3.3 Identification of individual components by retention time.
6.3.4 Noise and spike rejection capability.
6.3.5 Sampling rates for fast (<1 s) peaks.
6.3.6 Positive and negative sloping baseline correction.
6.3.7 Peak detection sensitivity for narrow and broad peaks.
6.3.8 Perpendicular drop and tangent skimming as needed.
6.4 Capillary Column - This test method utilizes a 50-m (0.21-mm inside diameter) fused silica capillary column with bonded (cross-linked) methyl silicone phase and a film thickness (df) of 0.5 µm. Other columns with these nominal dimensions may be suitable. However, all columns must meet the criteria set out in Section 10 for efficiency, resolution, and polarity.
7. Reagents and Materials
7.1 Carrier Gas, helium, 99.99 % pure. (Warning - Compressed gas under high pressure.)
7.2 Fuel Gas, hydrogen, 99.9 % pure. (Warning - Extremely flammable gas under pressure.)
7.3 Make-up Gas, helium or nitrogen, 99.99 % pure. (Warning - Compressed gases under higher pressure.)
7.4 n-Heptane, 99+ mol %. (Warning - Flammable. Harmful if inhaled.)
7.5 Methane - (Warning - Extremely flammable gas.)
7.6 2-Methylheptane, 99+ mol %. (Warning - Flammable. Harmful if inhaled.)
7.7 4-Methylheptane, 99+ mol %. (Warning - Flammable. Harmful if inhaled.)
7.8 2-Methylpentane, 99+ mol %. (Warning - Extremely flammable. Harmful if inhaled.)
7.9 n-Octane, 99+ mol %. (Warning - Flammable. Harmful if inhaled.)
7.10 Toluene, 99+ mol %. (Warning - Flammable. Vapor harmful.)
7.11 2,3,3-Trimethylpentane, 99+ mol %. (Warning - Extremely flammable. Harmful if inhaled.)
7.12 Column Evaluation Mixture, a qualitative synthetic mixture of pure liquid hydrocarbons with the following approximate composition-0.5 % toluene, 1 % n-heptane, 1 % 2,3,3-trimethylpentane, 1 % 2-methylheptane, 1 % 4-methylheptane, 1 % n-octane in 2-methylpentane solvent.
7.13 Reference Alkylate, actual refinery alkylation product used to prepare Fig. 1. (Warning - Extremely flammable. Harmful if inhaled.)
7.14 Reference Naphtha, actual refinery stream used to prepare Fig. 2. (Warning - Extremely flammable. Harmful if inhaled.)
7.15 Reference Reformate, actual refinery reformer product used to prepare Fig. 3. (Warning - Extremely flammable. Harmful if inhaled.)
8. Sampling
8.1 Hydrocarbon liquids (including naphthas) with Reid vapor pressures of 110 kPa (16 psi) or less may be sampled either into a floating piston cylinder or into an open container.
8.1.1 Cylinder Sampling - Refer to Test Method D3700 for instructions on transferring a representative sample of a hydrocarbon fluid from a source into a floating piston cylinder. Add inert gas to the ballast side of the floating piston cylinder to achieve a pressure of 350 kPa (45 psi) above the vapor pressure of the sample.
8.1.2 Open Container Sampling - Refer to Practice D4057 for instructions on manual sampling from bulk storage into open containers. Stopper container immediately after drawing sample.
8.2 Preserve the sample by cooling to approximately 4°C and by maintaining that temperature until immediately prior to analysis.
8.3 Transfer an aliquot of the cooled sample into a pre-cooled septum vial, then seal appropriately. Obtain the test specimen for analysis directly from the sealed septum vial, for either manual or automatic syringe injection.

