ASTM D4951 standard test method for determination of additive elements in lubricating oils by Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry (ICP-AES)
17. Precision and Bias
17.1 The precision of this test method was determined by statistical analysis of interlaboratory results. Fourteen participating laboratories analyzed twelve samples in duplicate. Most laboratories performed the analyses at three different levels of dilution, namely, 1 mass % sample in solvent, 2 mass % sample and 5 mass % sample. In this study, dilution solvents were limited to mixed xylenes, o-xylene, and kerosine. The most common source of organometallic standards was metal sulfonates. Most laboratories used a peristaltic pump, and approximately half of the laboratories used background correction. The sample set comprised eight oils, five of which were multi-grade oils, and four additive packages.
17.1.1 Repeatability - The difference between two test results, obtained by the same operator with the same apparatus under constant operating conditions on identical test material would, in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the values in Table 2 only in one case in twenty.
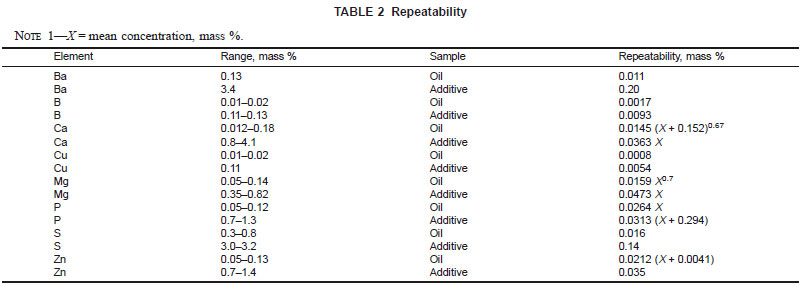
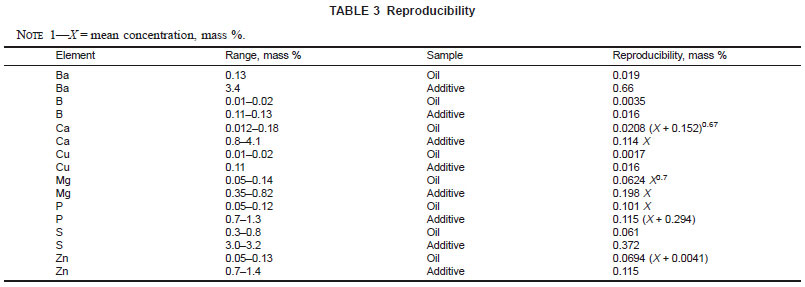
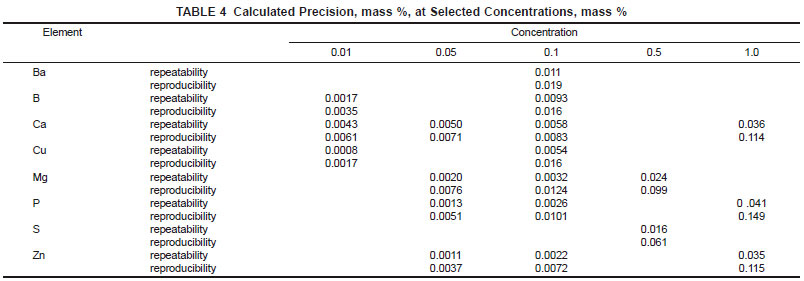
17.1.2 Reproducibility - The difference between two single and independent results, obtained by different operators working in different laboratories on identical test materials, would in the long run, in the normal and correct operation of the test method, exceed the values in Table 3 only in one case in twenty. (Also, see Table 4.)
 18. Keywords
18. Keywords18.1 additive-elements; barium; boron; calcium; copper; emission-spectrometry; ICP; inductively-coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry; internal standard; lubricating oils; magnesium; phosphorus; sulfur; zinc

